
¶ 1. Service and Support
This chapter provides information on the service and support of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO, desktop industrial grade 3D printers (hereinafter referred to as "FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO", the "printer", the "machine" or the "device"), as well as safety information and location of safety labels.
¶ 1.1 Service
If you have any questions not covered in this manual during the use of the printer, please contact INTAMSYS Customer Support:
| Region | |
| Asia-Pacific | Support_APAC@intamsys.com |
| Europe, Middle East and Africa | Support_EMEA@intamsys.com |
| America | Support_America@intamsys.com |
¶ 1.2 Safety Instructions
The following basic security tips are intended to ensure safe installation, operation, and maintenance of INTAMSYS equipment, and shall not be considered as comprehensive safety issues. The machine is a safe and reliable industrial grade 3D printer. Make sure to inspect for and eliminate potential hazards, if any, in the printer area before using this printer.
¶ 1.2.1 Hazard type
INTAMSYS recommends that all services be provided by qualified personnel. All personnel who operate this printer or are near it shall understand the meaning of the following hazard classification signs used in this manual.
 |
[High Voltage Warning]: It indicates that high voltage exists. Keep away from exposed circuits, and it is recommended to remove all ornaments. |
 |
[High Temperature Warning]: It indicates a high printer temperature. Be cautious when working near components that are exposed to heat. Always wear the safety gloves that come with the printer. The temperature of the print head in the printer can reach up to 300℃. The temperature of the printing platform in the printer can reach up to 160°C. The temperature in the chamber of the printer can reach up to 100°C. |
 |
[Pinching Warning]: It indicates that your hands might be pinched between two objects. One or more objects are moving in your working area. |
Please note that changes or modifications without the approval of the responsible party for compliance may invalidate the user's permission to operate the device.
- The device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and the Industry Canada License-exempt RSS Standard. The following two conditions should be met for operation:
1. The device may not cause harmful interference;
2. The device must accept any interference received, including interference that may lead to undesired operation.
- The device complies with the radiation exposure limits of FCC/IC RSS-102 for uncontrolled environment. The device shall be installed and operated at a minimum distance of 20 cm from the radiator and the operator
¶ 1.2.2 Areas with potential safety hazard
The following components and areas have been highlighted as with potential hazards. Failure to follow the safety regulations might cause system faults or reliability issues.
|
Extruder  |
 |
[High Temperature Warning]: Make sure to wear safety gloves if it is necessary to maintain the extruder or work inside the chamber when the extruder is heated. |
|
Printing Platform 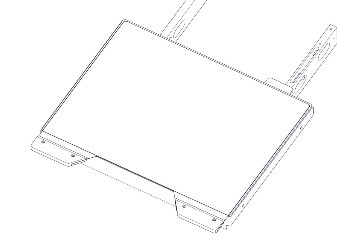 |
 |
[High Temperature Warning]: Make sure to wear safety gloves if it is necessary to remove the printing build plate of the platform or work inside the chamber when the hot bed is high in temperature. |
|
Chamber  |
 |
[High Temperature Warning]: Make sure to wear safety gloves if you work inside the chamber at medium and low temperatures during heating; it is not recommended to work in the chamber at high temperatures. |
|
XY Motion Frame 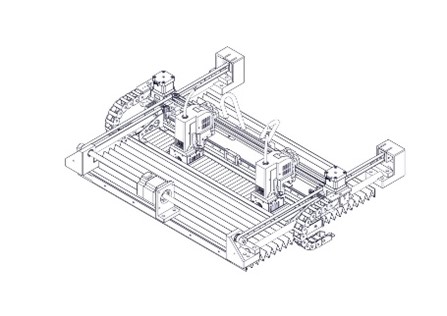 |
 |
[Pinching Warning]: Do not wear tie, loose clothing, or hanging ornaments when working near a moving printer component. [Pinching Warning]: Do not click HOME when there is a model on the platform. [Pinching Warning]: Be careful when maintaining this moving component. |
|
Z-axis Motion Frame  |
 |
[Pinching Sign]: Do not wear tie, loose clothing, or hanging ornaments when working near a moving printer component. [Avoid Collision]: If there is a printed model on the platform, be care to raise the platform to a proper height to prevent puncturing the organ cover; [Avoid Collision]: If there is an object under the platform, be care to lower the platform to a proper height to prevent deformation of drive rod parts and leveling failure caused by platform collision. |
¶ 1.2.3 Safety door lock
Sensors are used to monitor the status of the chamber front door and printer top cover. For the purpose of safety, the chamber door and top cover shall be closed before the XYZ motor can start working. The electromagnetic lock ensures that the chamber door and top cover remain securely closed during printing.

¶ 1.2.4 Environmental requirements
- The printer is for indoor use only.
- Air quality conditions (conductive or non-conductive) with excessive solid particles might cause damage to the system.
- The printer shall operate between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F) with a relative humidity range of 30% to 70% (non-condensing).
- The printer storage temperature shall be between 0°C and 35°C (32°F to 95°F) with a relative humidity range of 20% to 90% (non-condensing).
¶ 2 Setting and Installation
This chapter describes the basic settings and installation of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO.
¶ 2.1 General Information
¶ 2.1.1 Tools that come with the printer
Please check the packing list that comes with the printer. These tools include common tools required for printer maintenance and various spare parts.
¶ 2.1.2 Prepare relevant equipment for installation
The guide for preparation of installation site ensures that relevant equipment for printer installation can be prepared effectively and safely.
 |
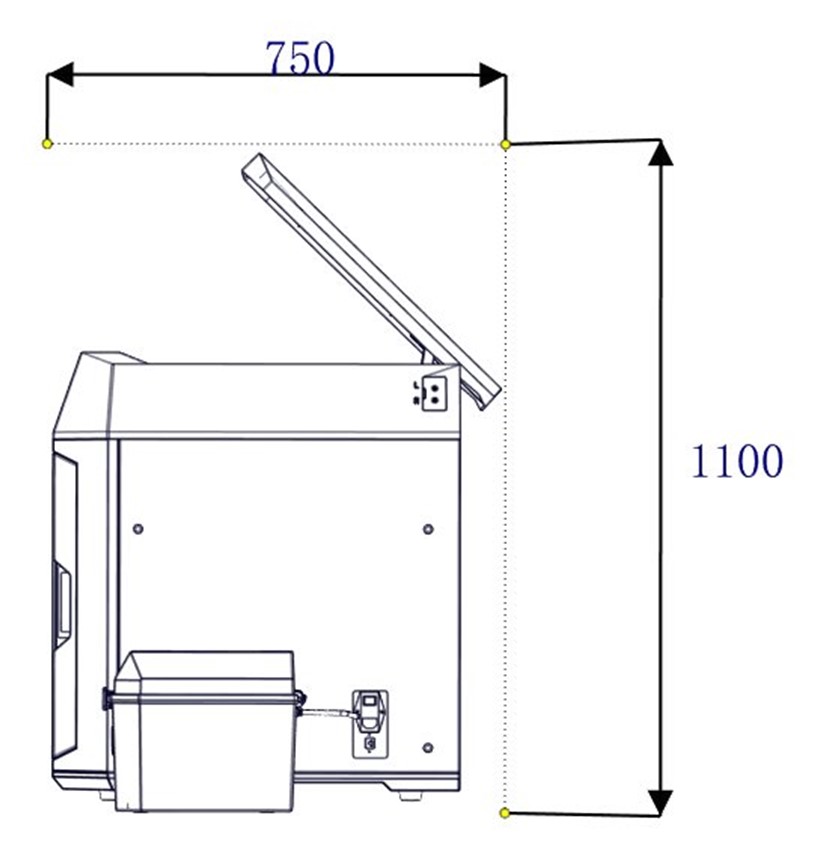 |
| Figure 2.2 Space required for installation and maintenance (Unit: mm) | |
¶ 2.1.3 Check the printer nameplate
Refer to the figure below to identify your printer.
Model information: Product name, model number and power requirements. This nameplate also lists the relevant certifications and INTAMSYS information.
SKU: Lists the SKU of the printer. Upon a service request, provide this SKU to the agent or INTAMSYS, so that service personnel can quickly identify your printer configuration.

¶ 2.2 Printer Preparation
¶ 2.2.1 Unpack
Step 1: Remove the protective film and fixing tape on the outside of the packaging box.
Step 2: Remove the wooden board at the top of the packaging box and the top cover of the packaging box in sequence.
Step 3: Remove the cardboard and foam around the packing box.
Lift the printer from the bottom and place it to a stable platform (at least two people are required).
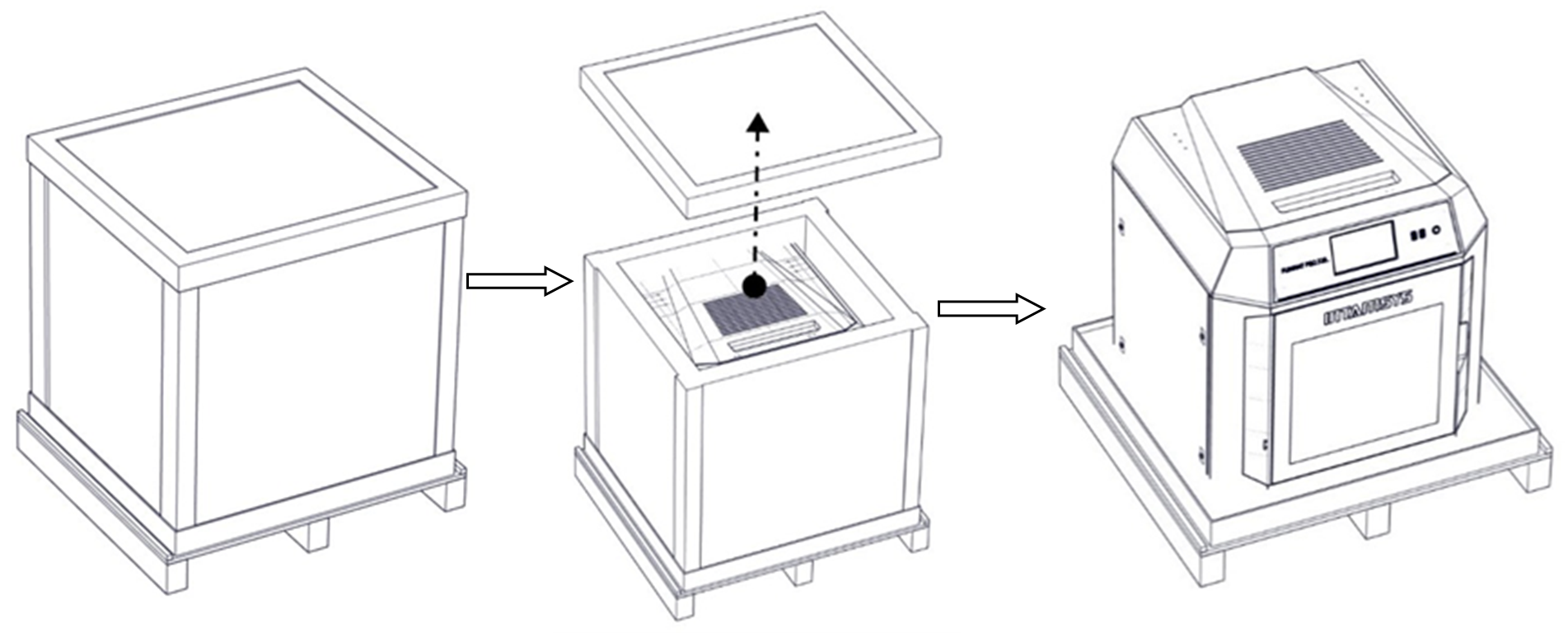
¶ 2.2.2 Remove accessories
Open the front door of the device from the front, and carefully take out the accompanying accessories and material boxes. As the platform would be tightly compressed against internally packaged foam cotton due to the impact of vibration and self-gravity during transportation, the machine shall be energized to raise and reset the platform before removing the accompanying accessories and material boxes. Refer to the Quick Start Guide for this step.

¶ 2.2.3 Unbuckle X-axis and Y-axis
Step 1: Open the top cover of the printer;
Step 2: The fixing block on the X-axis guide rail is used to ensure the stability of the extruder during transportation. Unscrew the two screws on the fixing block with a 3 mm Allen wrench (the Allen wrench is placed in the spare parts box), and then remove the X-axis fixing block.
Step 3: Remove the Y-axis fixing block fixed on the front side sheet metal in the same way.
Step 4: When the power is off, gently push the print head leftward in X direction to move out enough operating space, and remove the right fixing block of Y-axis with the same method;

Step 5: Install the left and right extruders in the extruder holder as shown in the figure;

Step 6: Rotate the pressure levers on both sides of the extruder holder upward to fix the extruder in the extruder holder, and plug in the extruder cable.

¶ 2.2.4 Startup
Step 1: The printer has two power specifications: 110V and 220V. Please make sure to check whether the socket power supply meets the requirements before use.
Step 2: Insert one end of the power cord into the right power supply port of the printer, and insert the other end into the power socket prepared in advance.
Step 3: Turn on the switch and press the start button at the lower right of the printer to enter the operation interface;

¶ 2.2.5 Installation of Printing Build Plate
Step 1: Enter the "Tools" interface on the right in the main interface, and click the "Home All" button (make sure that there are no other sundries in the chamber before operation);

|

|
Step 2: After selecting the "Z Build Plate" option in the upper part, click "Z-Bottom" to move the printing platform to the bottom of the chamber;
Step 3:According to the diagram, remove the buckle devices on both sides of the platform.

|

|
Step 4: Flatly adsorb the printing build plate above the magnetic platform along the guide grooves on both sides of the platform, as shown in the figure.

|

|
¶ 3 System Components
This chapter describes the system components of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO, aiming to help users better understand the mechanism composition of the printer and the functions of each part.
¶ 3.1 Printer Overview
The visible parts of the printer is shown in the following figure, where:
The right side plate, left side plate and rear side plate of the housing are removable for access to internal components; the top door and front door must be closed during printing and locked by electromagnetic locks.


¶ 3.2 Top Door and User Operation Interface
Push the top door upward to observe the movement of extruder from above and for the maintenance of XY rack and print head assembly.
By releasing the electromagnetic lock through screen operation, the top door can be pushed upward and supported by damping hinges. The damping hinge can ensure that the top door stops at any opening or closing position.
Below the top door is the user interaction area, which includes touch screen, USB interface and ON/OFF switch.
Users can control the print part and obtain the machine status information through the touch screen. The USB on the left is only used to connect to computers for printing and firmware upgrade, while the USB on the right is used to insert a U-disk for printing. The ON/OFF switch is used for startup and shutdown, as well as emergency shutdown.

|

|
¶ 3.3 Printing Chamber Components
The front door can be pulled open from the right side by the release of the electromagnetic suction of the front door through screen operation, and then it can be seen that the printing chamber contains front door, hot bed, double extruder assembly, electromagnetic suction, magnetic suction and door sensor.
When the printing chamber is heated, its stainless steel build plate and side plates are hot. Please do not touch them to avoid scalding.
The four leveling knobs under the hot bed are used to manually level the printing platform.

|

|
¶ 3.4 Printing Head Assembly
The print head assembly is used to melt the filament and form a desired model on the printing buildplate in combination with the movement of X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis. A machine contains two separate print heads, generally the left extruder for printing model material and the right extruder for printing support material. Generally, there's only one extruder performing printing at the same time point, while the other extruder stands by at the end of X-axis. When copying or mirror printing is carried out, the two extruders move simultaneously.
Refer to Chapter 4 for loading and unloading of materials.

¶ 3.5 X/Y Axis Components
X-axis and Y-axis components drive the double-extruder to move within the XY plane according to commands.
X-axis and Y-axis are driven by the synchronous belts, whose tension has been properly adjusted at factory and does not need to be re-adjusted during use. After a period of use, if the printing quality is found to have degraded significantly, the likely cause is the synchronous belts becoming loose due to various reasons. In this case, remove the left and right lateral plates of the printer and check the tension of the left and right synchronous belts of Y-axis; After removing the rear housing, you can adjust the tension of the Y-direction synchronous belt. Open the top door to see and check the tension of the synchronous belt of X-axis. If the tension of a synchronous belt is found too small, you can increase the tension using the method shown in the figure below. The left and right synchronous belts of Y-axis shall keep a consistent tension.
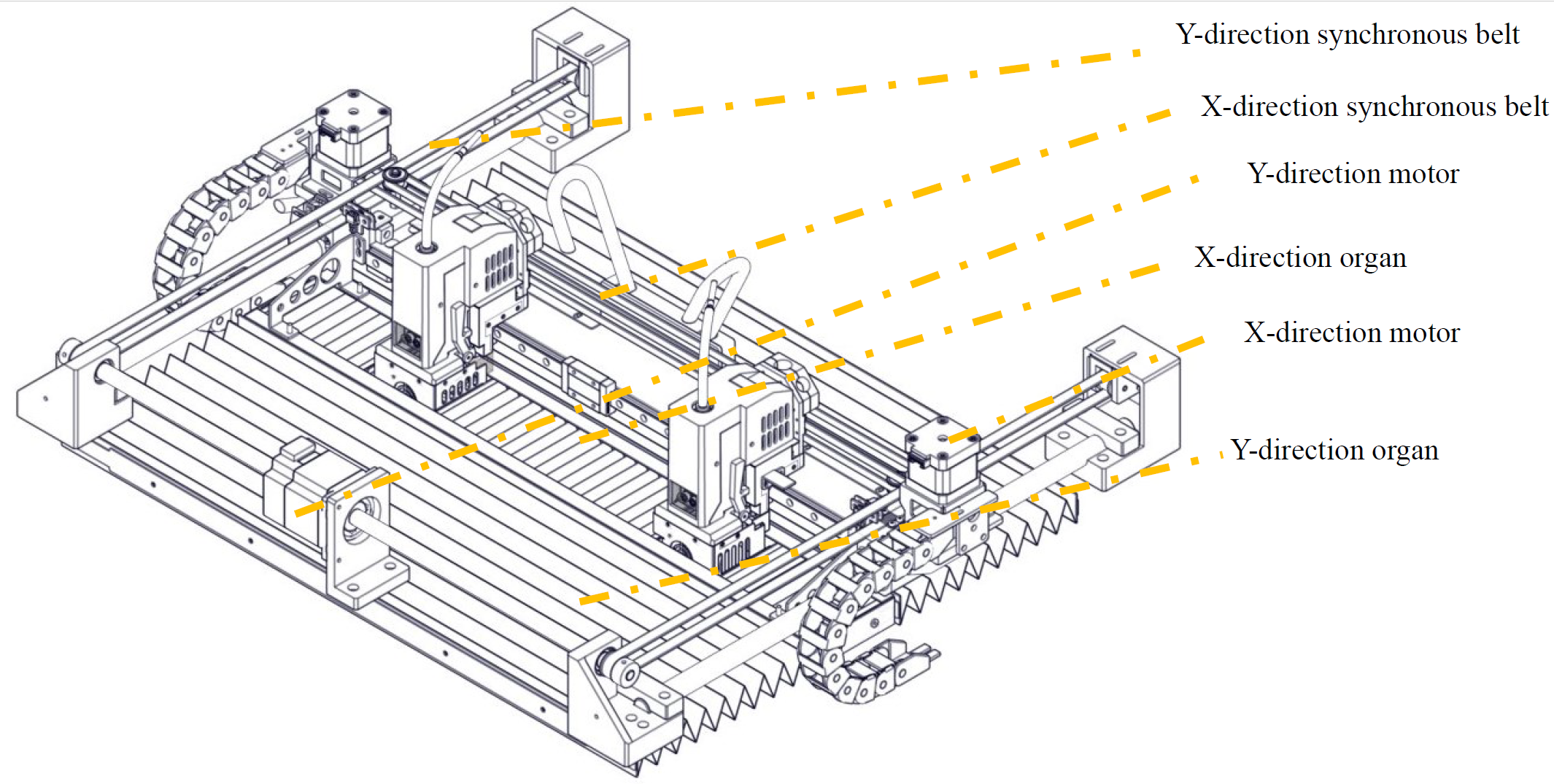


¶ 3.6 Z-axis Components
The Z-axis components drives the hot bed to move up and down. Remove the back lateral plate to maintain the Z-axis components when necessary.
The trigger plate of the photoelectric sensor is already in place and generally does not need to be adjusted by the user. Only when problems are encountered with manual leveling of the hot bed may it be necessary for the user to check and adjust the trigger plate position appropriately. Adjusting the trigger plate of the photoelectric sensor upward enables the zero position of the hot bed to move downward, and adjusting the trigger plate of the photoelectric sensor downward enables the zero position of the hot bed to move upward.

¶ 3.7 Hot Bed Components
The hot bed components consist of printing build plate, high-temperature resistant magnet, coaming and heating film. The printing build plate of the printer is a magnetic plate, and 18 high-temperature resistant magnets are installed on the hot bed substrate, which can adsorb the printing build plate to the hot bed substrate in a flat and firm manner. The hot bed substrate has four leveling screws. Manually level these screws according to the guidance of the operation interface when necessary.

¶ 3.8 Independent Filament Box
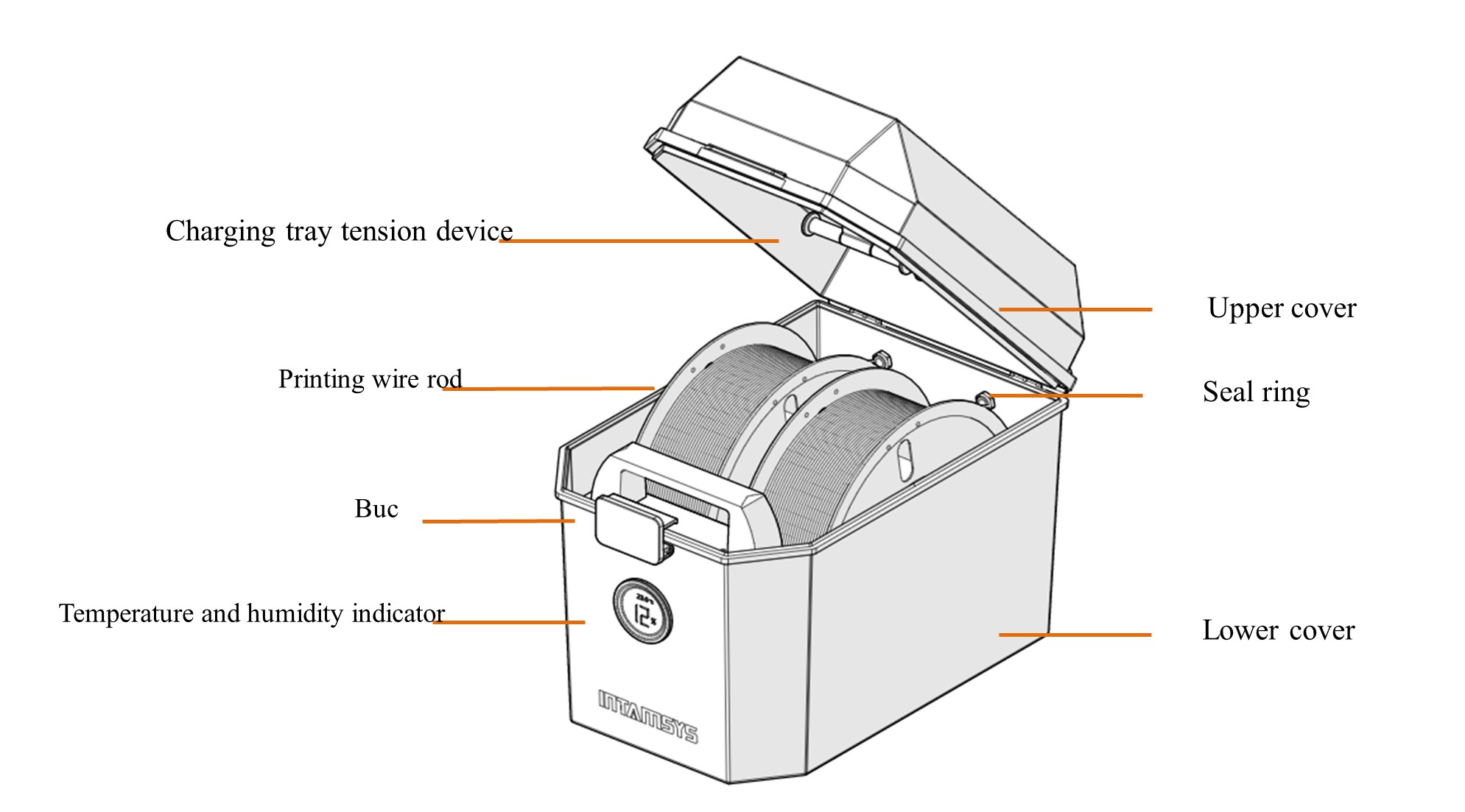
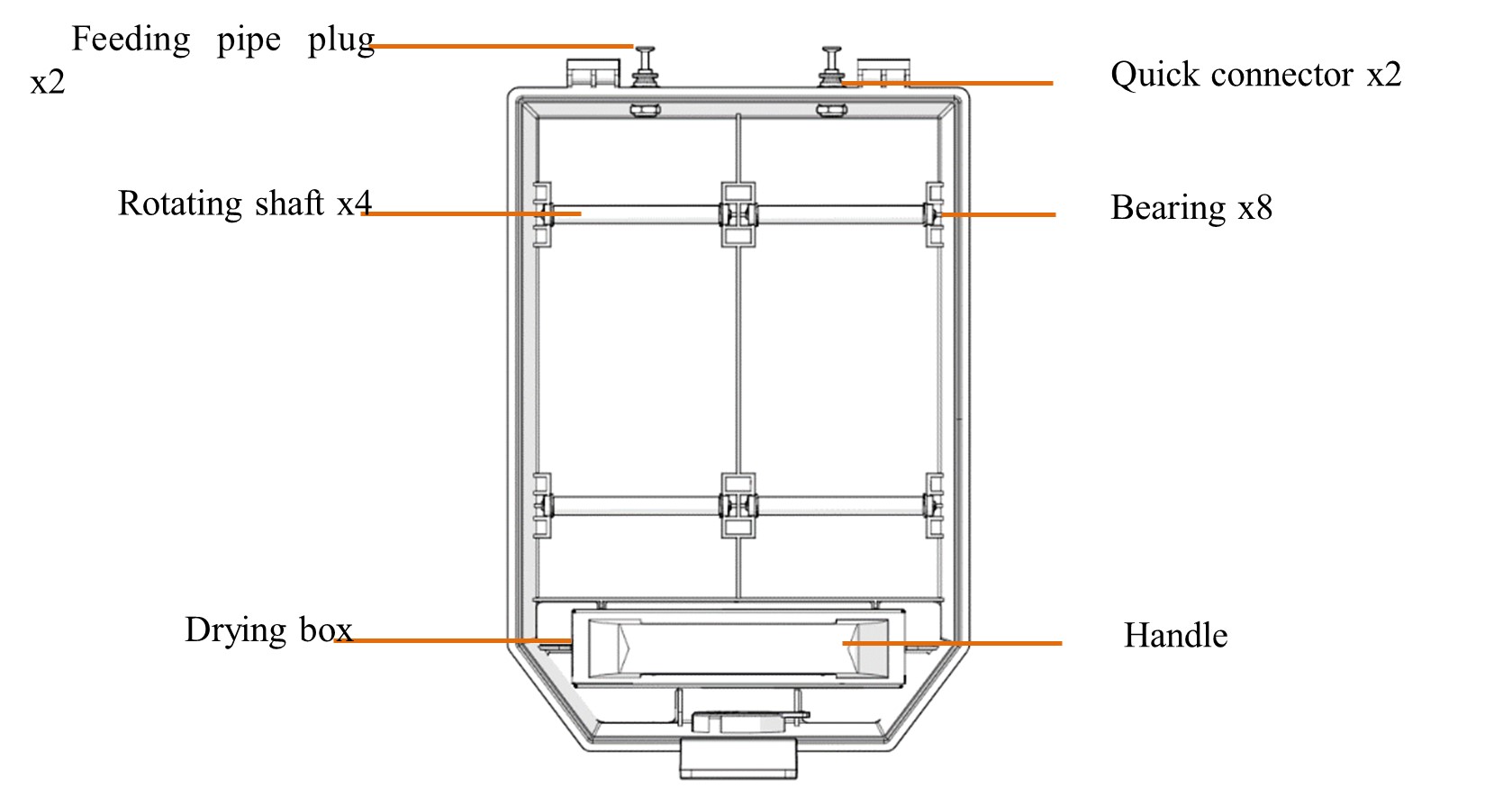
The printer is supplied with an external INTAMBox Sealed Drying Filament box that can hold up to two rolls of 1 kg material. Seal rings and buckles are provided around the filament box to ensure its sealing performance. The filament box is supplied with a drying box filled with 4A molecular sieve desiccant, which can ensure the low humidity environment inside the filament box. The upper cover of the filament box is equipped with a charging tray tension device to ensure that the printing wire rod will not be loosen during printing and that the wire coil will not topple when the wire rod in the wire coil are used up. Please refer to the Operation Manual of INTAMBox Sealed Drying Filament box for details.
¶ 4 User Interface
¶ 4.1. Overview
This chapter describes the main user interface (UI) of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO. For the specific printer operation information and programs, you can refer to Chapter 5. The printer must be powered on before using the touch screen.
FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO user interface consists of a touch screen located in the middle of the front side of the printer. The main interface of the touch screen includes three main functional areas: status bar, navigation bar and display area.
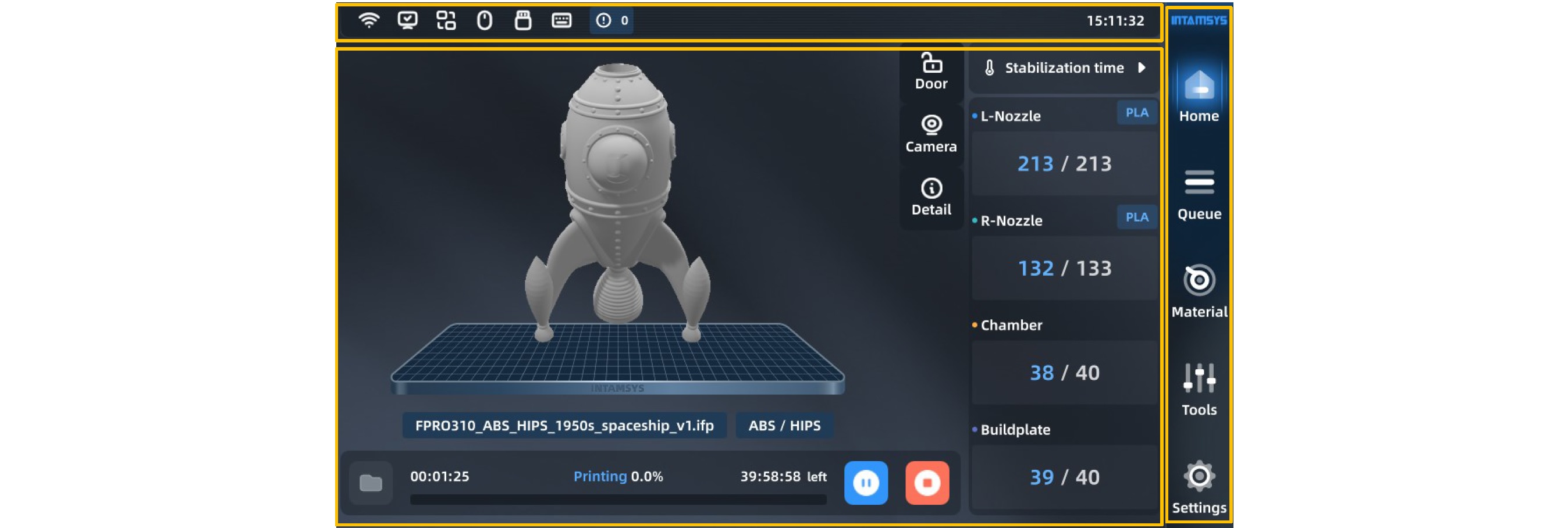
The status bar is docked to the top of the touch screen display. On the status bar, in addition to viewing Wi-Fi, U-disk and network status, you can also view alarm information. The navigation bar is on the right side of the panel, where you can access main functions through corresponding commands.
In the display area, you can select the G-code file to be printed, start/pause/stop printing, and preview the printing status on the model picture.
¶ 4.1.1 Status bar
The status bar is docked to the top of the touch screen display and appears on each page of the user interface. It displays various information including network status indicators, cameras and USB flash memory.

¶ 4.1.2 Navigation bar
|
You can perform the following operations through the navigation bar on the screen.
Homepage: Printing operation, preheating and heat hold settings, model graphic progress display, real-time status display, etc.
Queue: You can manage G-code/print file import and print order, and engineers can manage their daily work tasks in the queue.
Materials: You can carry out material selection, loading and unloading, material database management and other materials-related operations in this interface.
Tools: In this interface, you can control each moving axis of the printer and nozzle extrusion operation, as well as print calibration and parameter setting related operations.
Settings: You can view system parameters and make relevant system settings.
|
 |
¶ 4.1.3 Display area
The display area displays the related information corresponding to the selected function module, including operation buttons, texts, images, or schematic GIF, etc.
After the machine is powered on and started, it will automatically enter the main interface.
When you select a function button in the navigation bar, the display area switches to the corresponding interface.
If there is no screen operation for 10 minutes, the system will automatically call the Screen Saver (the screen protecting time can be set in the setting interface). Touch the screen again to return to the main interface.
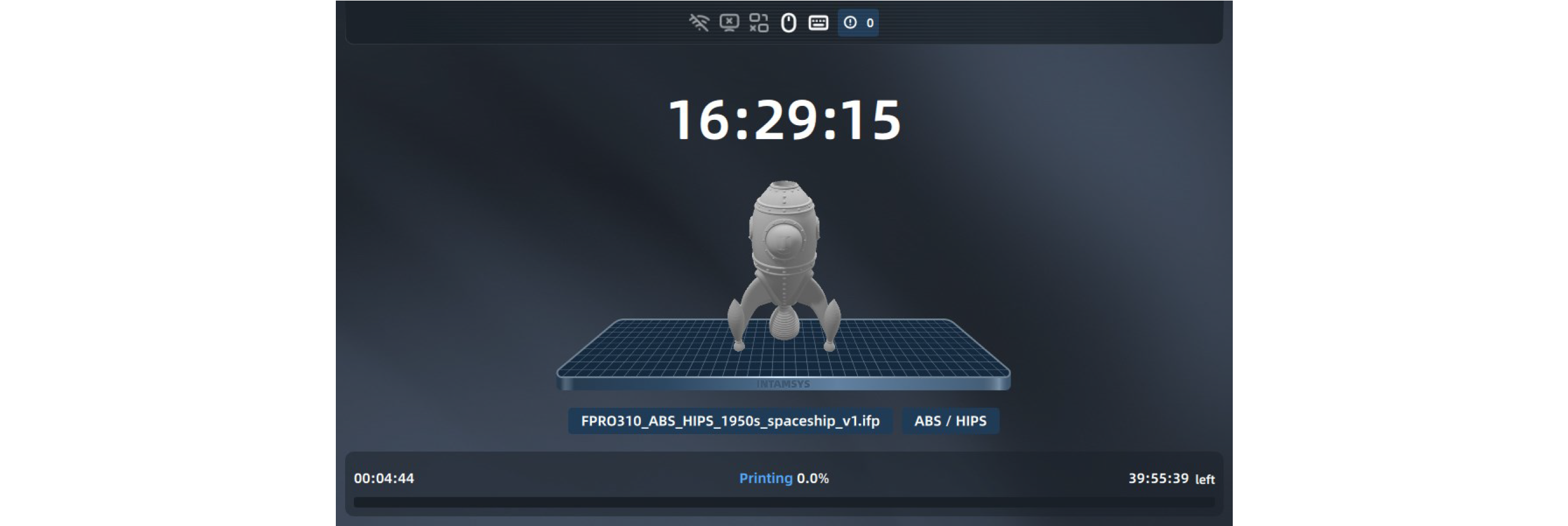
¶ 4.2 Main Interface
The homepage interface mainly displays the overall information of the device during printing. The left area includes model print progress preview and print operation buttons, which are used to start/pause/stop printing.
The real-time temperature status of the printer is displayed in the right area, including L-nozzle temperature, R-nozzle temperature, chamber temperature and hot bed temperature.
The current connection status of the device is displayed by the icon on the top. If an error alarm occurs during printing, it will also be displayed in this bar.
Touch the screen to view and operate other functions displayed on the main interface.
¶ 4.2.1 Loading print files
| FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO provides two methods to load USB and locally stored print files. Click “folder” icon to select the file acquisition method, and find the print file by reading USB storage or printer local storage. You can choose to press "Print" to load the print file for immediate printing, or press "Add to Queue" to load the file into the queue for subsequent printing. |
 |
| The print file format can be .gcode or .ifp. For .ifp format file, you can preview the model shape and the print progress can be displayed during printing. | |
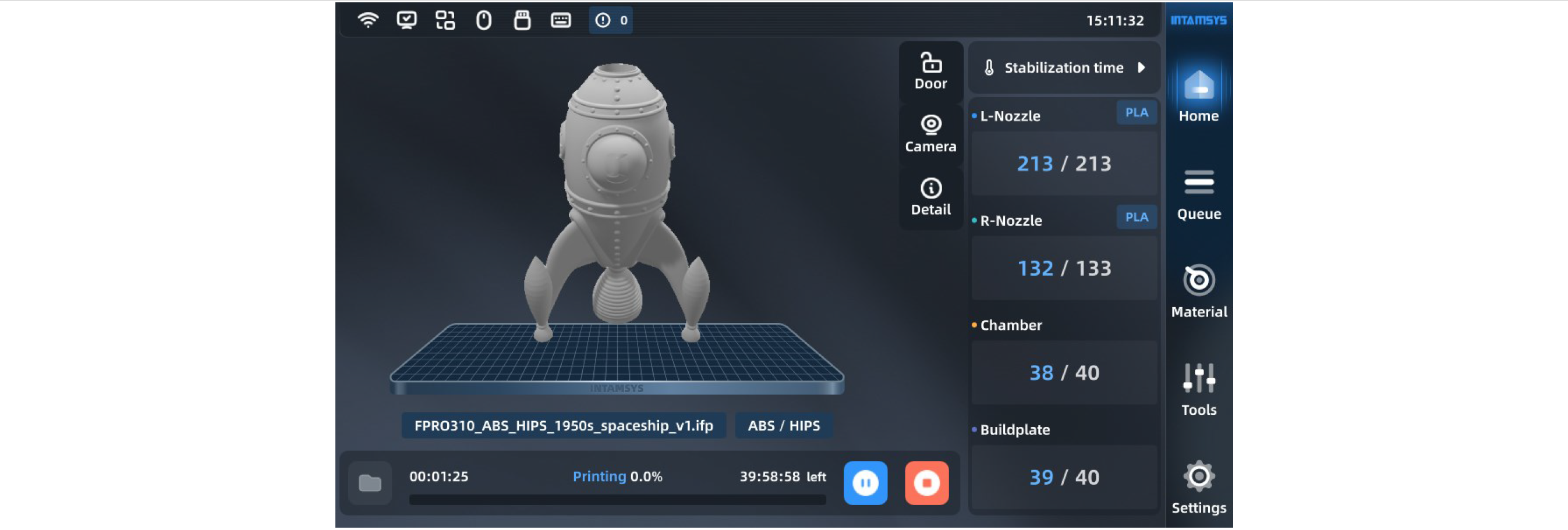
¶ 4.2.2 Main status area
The main status area can display model pictures and show print progress by filling color. The model is completely filled to indicate that the print job is complete. If the model cannot be displayed, the system will display a default image. The file name and materials required for printing are displayed below the model picture.
There are three easy buttons in the upper right corner that allow us to lock the front door, display camera video and view details related to print files.

¶ 4.2.3 Auxiliary status area
|
The auxiliary status area displays the temperature of L-Nozzle, R-Nozzle, chamber and hot bed. The current temperature is displayed on the left, and the target temperature is displayed on the right. The arrow icon and fill color animation indicate the progress of heating/cooling, and it will be fully filled with the color if the target temperature is reached. The loaded material is displayed on the right side of the nozzle temperature, and we can quickly know the model number of the material installed in the filament box.
|

|
| In order to obtain better printing quality, we can set the preheating stabilization time of the chamber before printing and the heat hold maintenance time of the chamber after printing. We can also set the built-in time of the device, or disable it or adjust its duration as needed. | |
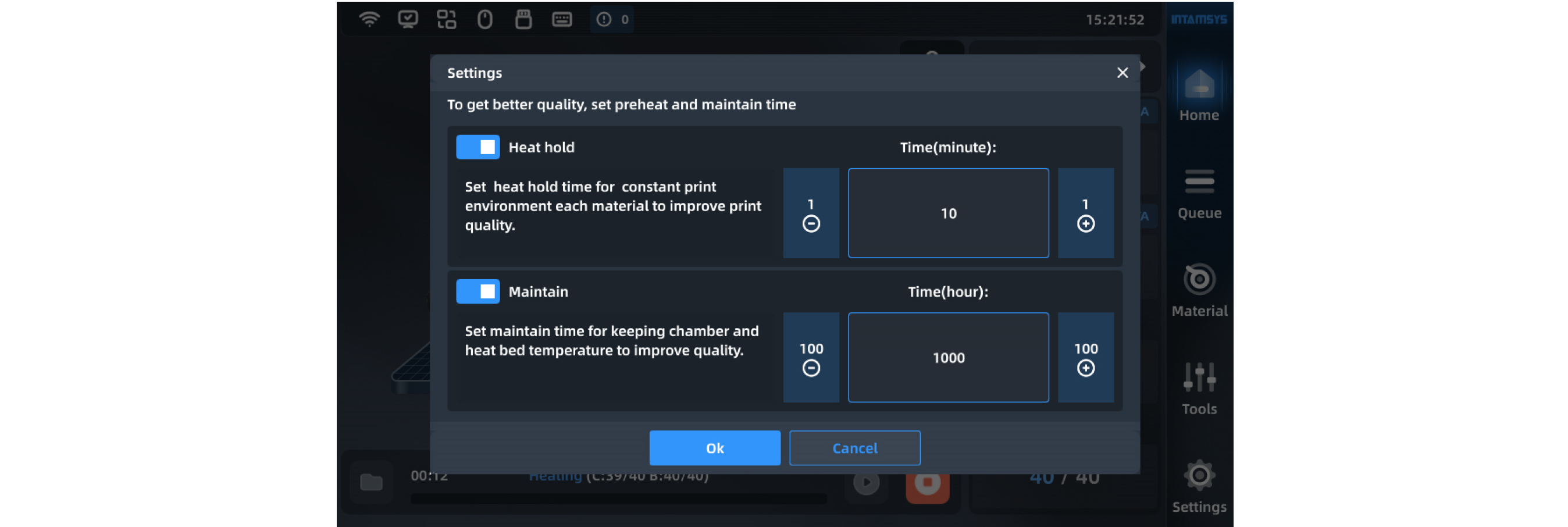
|
|
¶ 4.2.4 Control area
|
The bottom control area includes "Open", "Start" and "Stop" buttons as well as a progress bar to control or check the printing progress. Click the "Open" button and enter the "File Navigation" interface to open the file. The Start/Pause/Stop buttons are available during the printing phase. Task progress and consumed/remaining time are shown on the progress bar. When the print task is completed, a command to reprint or perform the next task in the queue will be displayed. |
 |
 |
 |

|
|||
¶ 4.3 Queue
It includes sample queue, current task queue and task history.
In the sample queue, print sample files are provided for printer testing. The order of print files or samples cannot be modified in the sample queue.
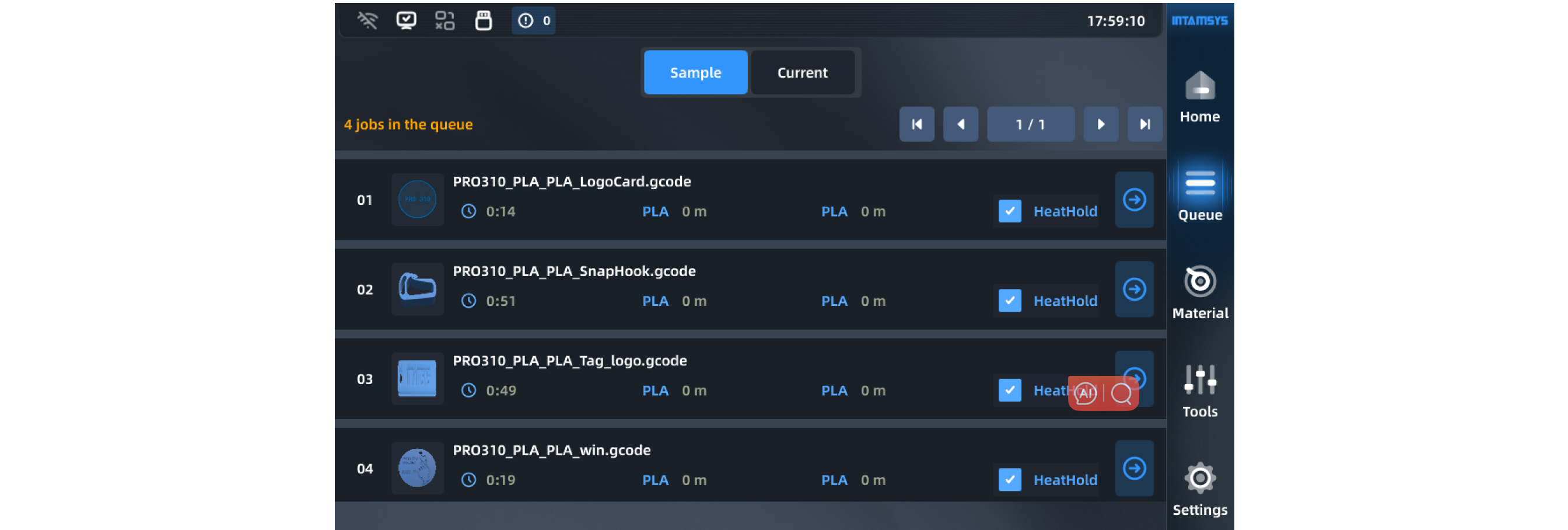
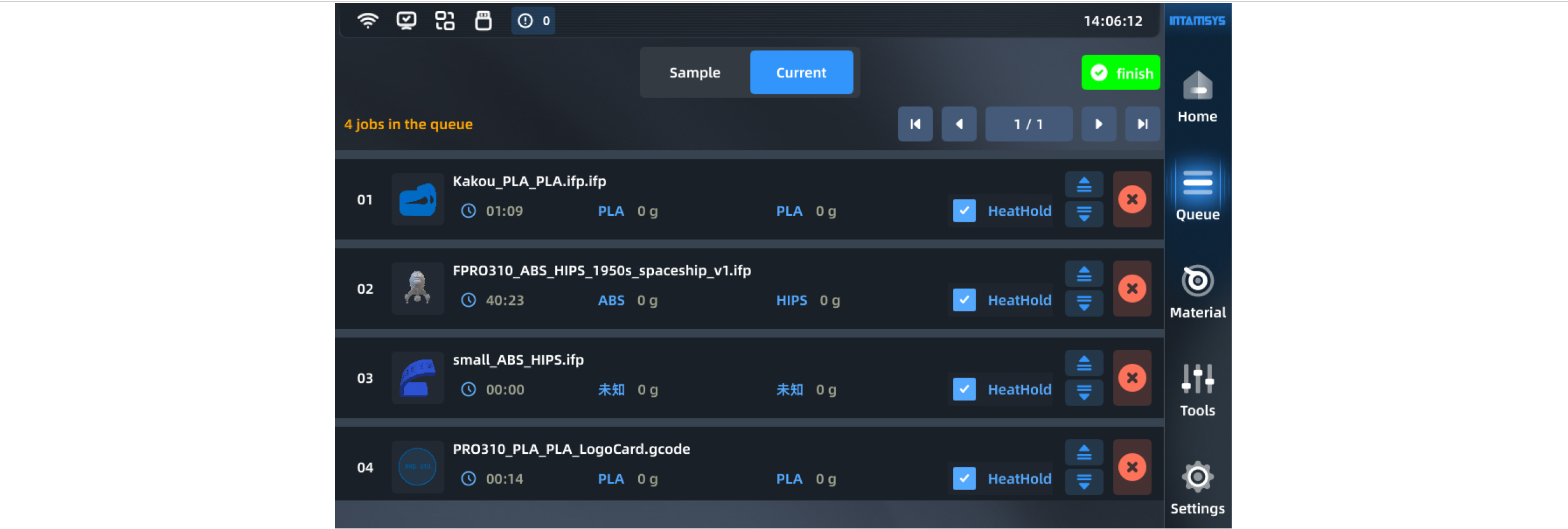
In the current task queue, import and edit commands are provided in the upper right corner. You can add files or adjust the order of tasks. Once the current task is completed in the queue, the next task will be automatically listed.

¶ 4.4 Materials
You can carry out material setting, material loading and unloading, and material database management on the material interface.
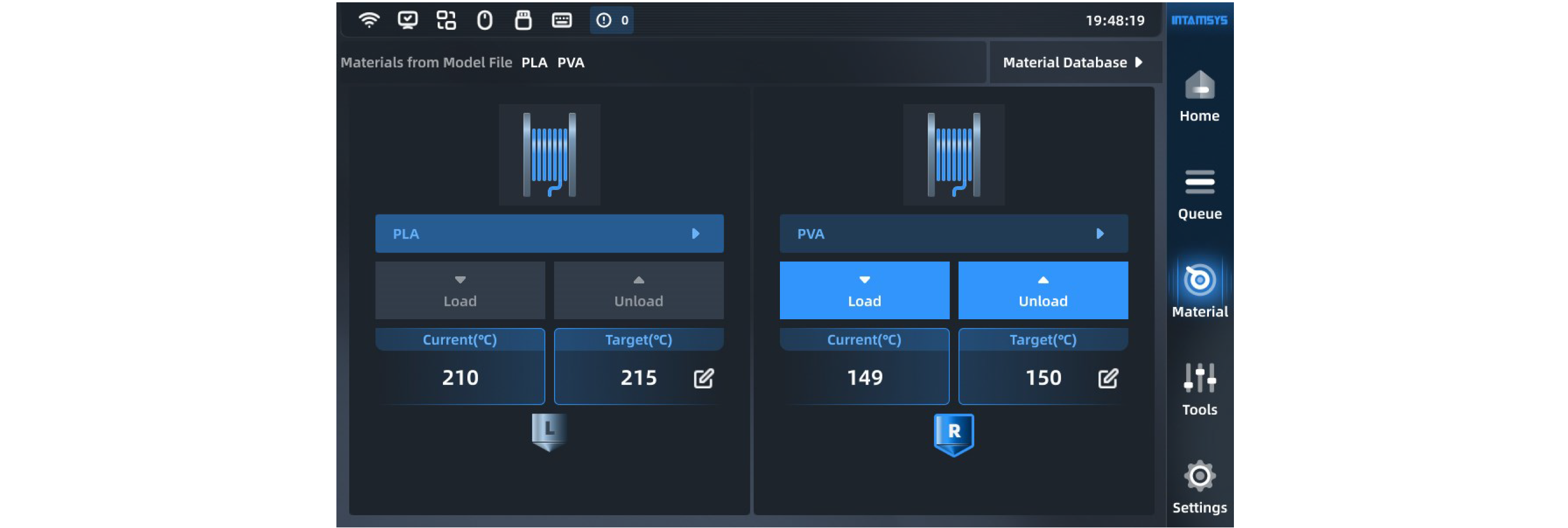
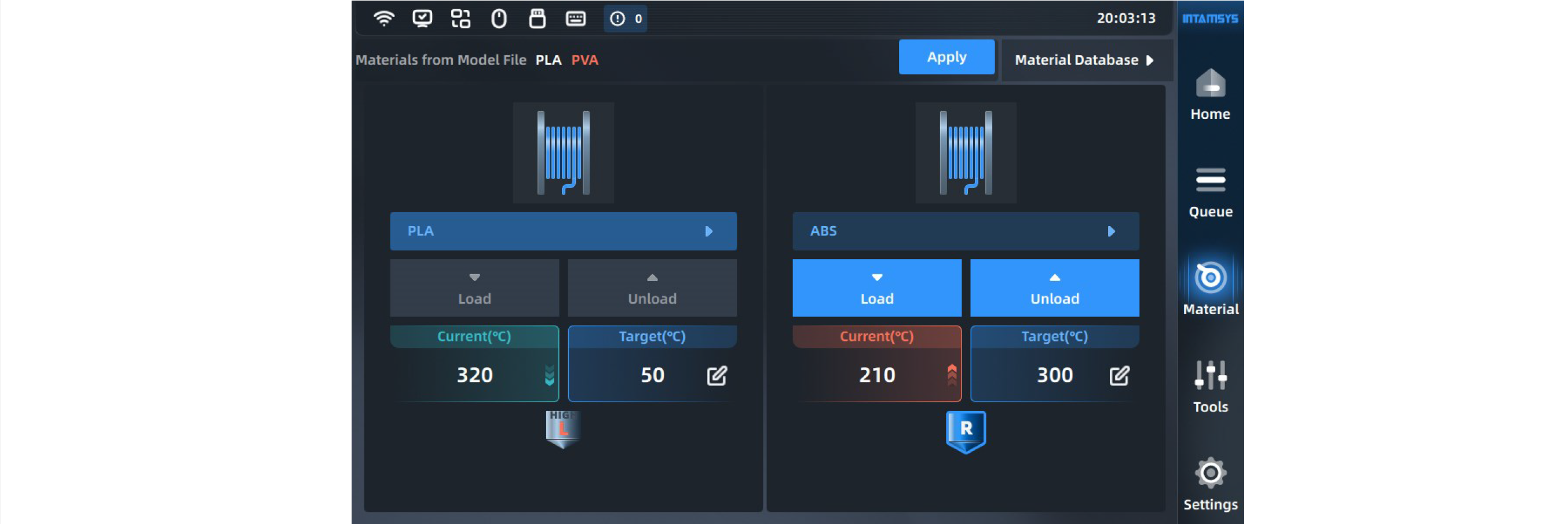
¶ 4.4.1 Material selection
Pressing the material name list button will display INTAMSYS materials and user-defined materials. Materials that were used recently and frequently will be displayed at the top, where we can scroll down to select all available materials.
User-defined materials can be configured in the material database.
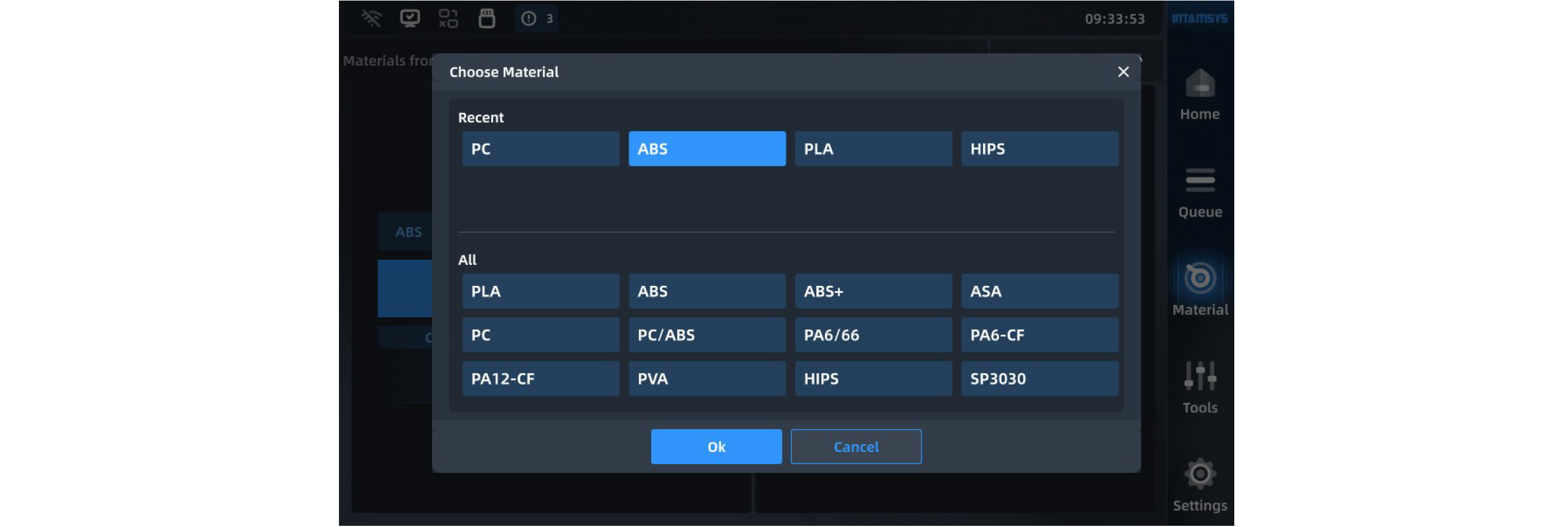
Specifically, if the material on the printer is inconsistent with the material settings in the G-code print file, it will alert the user to apply the material. Press "Apply", and the printer will automatically recognize and apply the correct material to the L-Nozzle and R-Nozzle.
Note: We need to unload/load the corresponding materials manually.
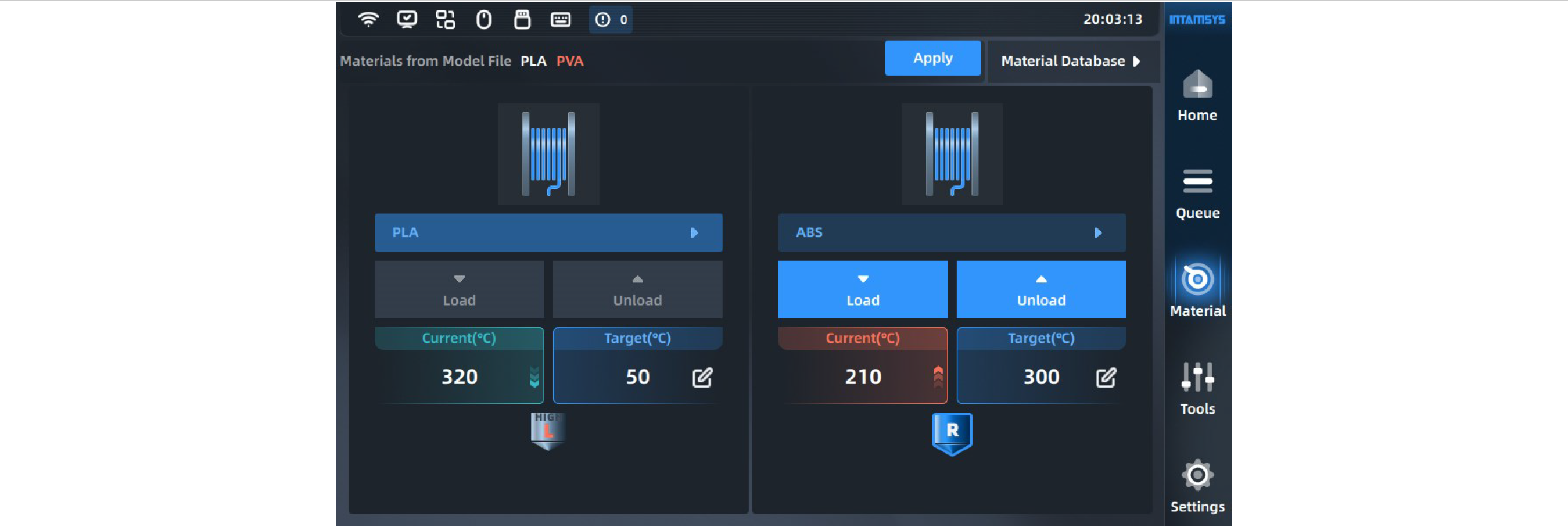
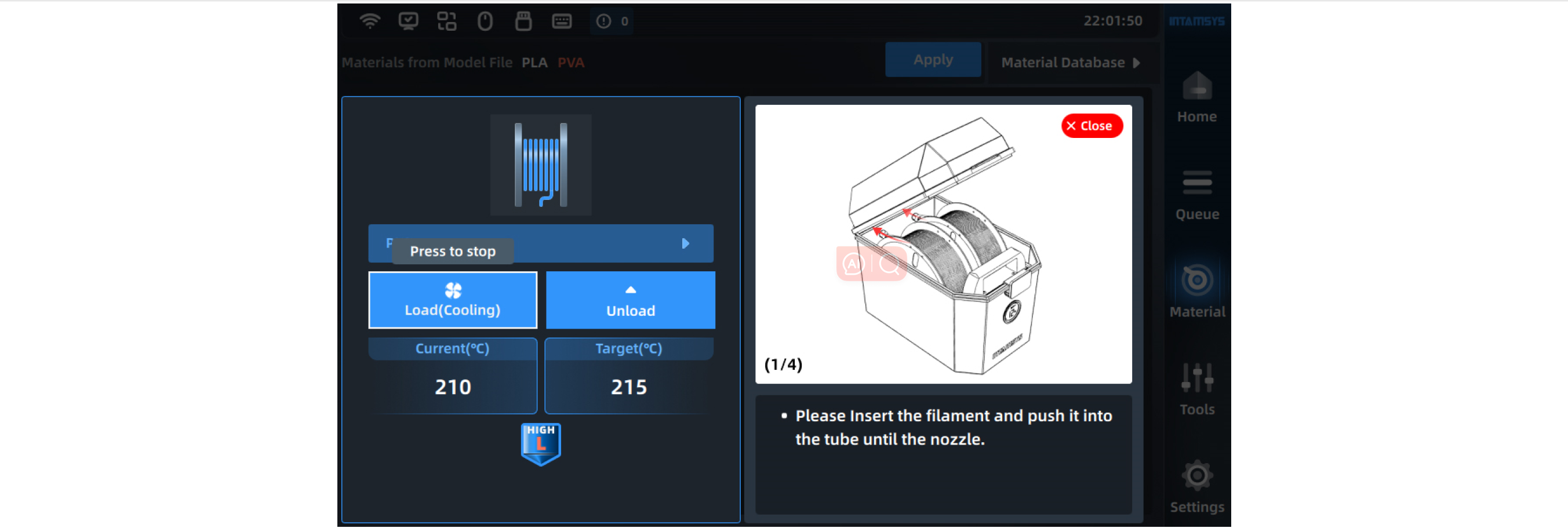
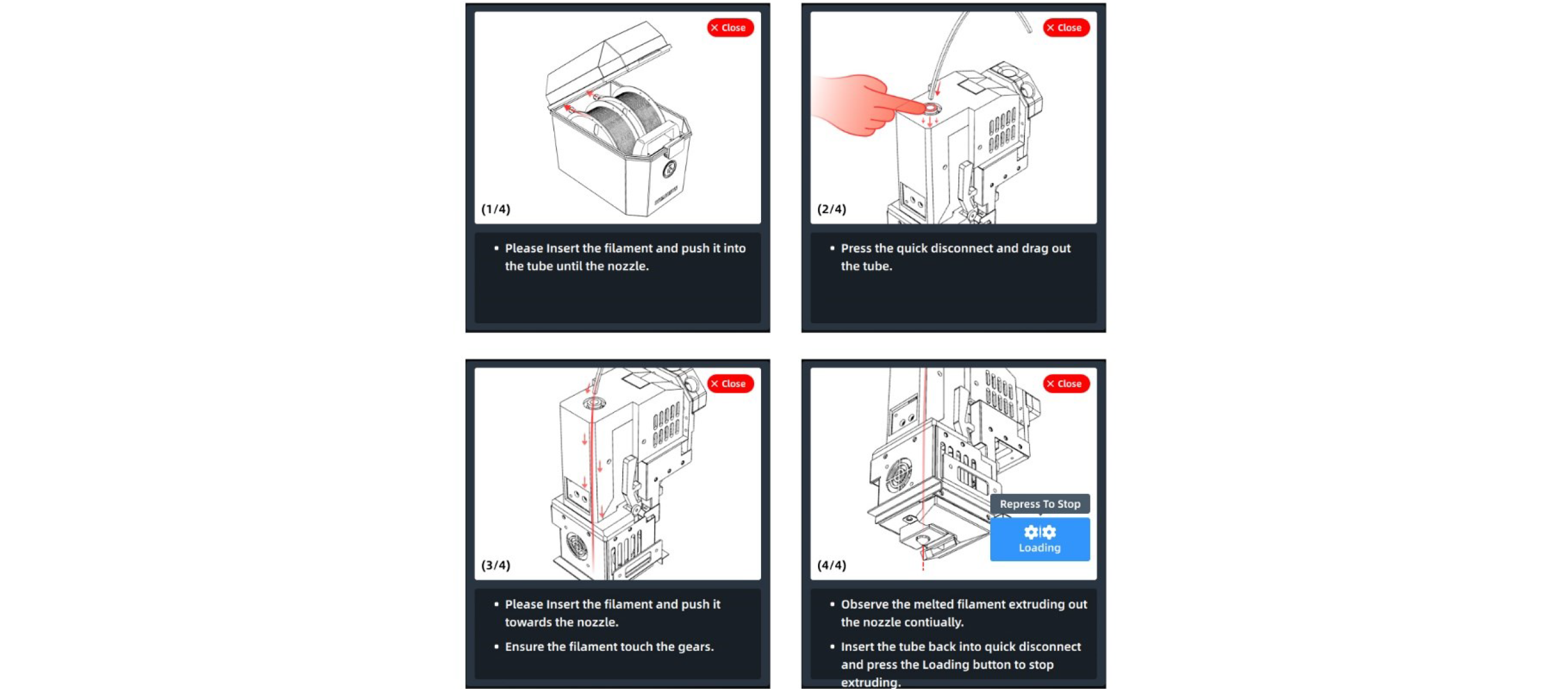
¶ 4.4.2 Material loading
After preparing the required material, correctly select the name of the required materials in the material interface, and click the "Load" button to automatically heat the nozzle to the target temperature and perform operations according to the prompts on the right side. Click the "Load" button again or other blank area to exit the loading process.
After getting familiar with the operation, the user can close the prompt window, which will be folded, and open it again if necessary.
¶ 4.4.3 Material unloading
The material unloading process is similar to loading. Press the "Unload" button and unload the filament step by step according to the wizard tips.
NOTE: First feed and then unload the filament to prevent the materials in the nozzle from carbonizing.
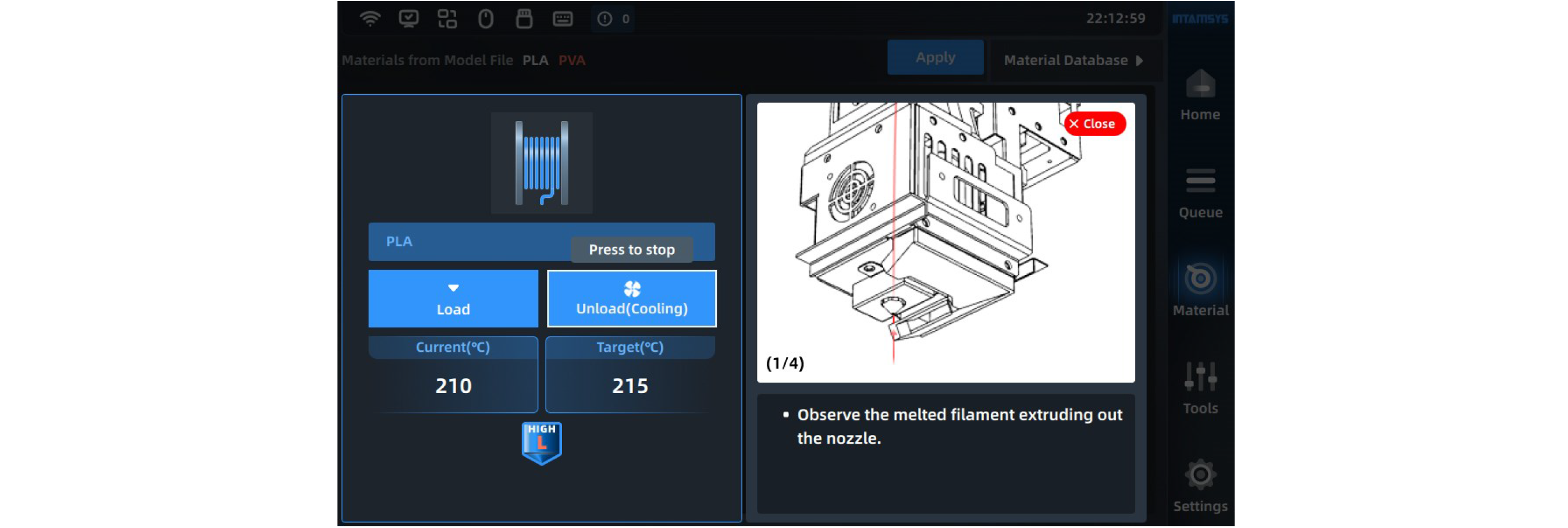
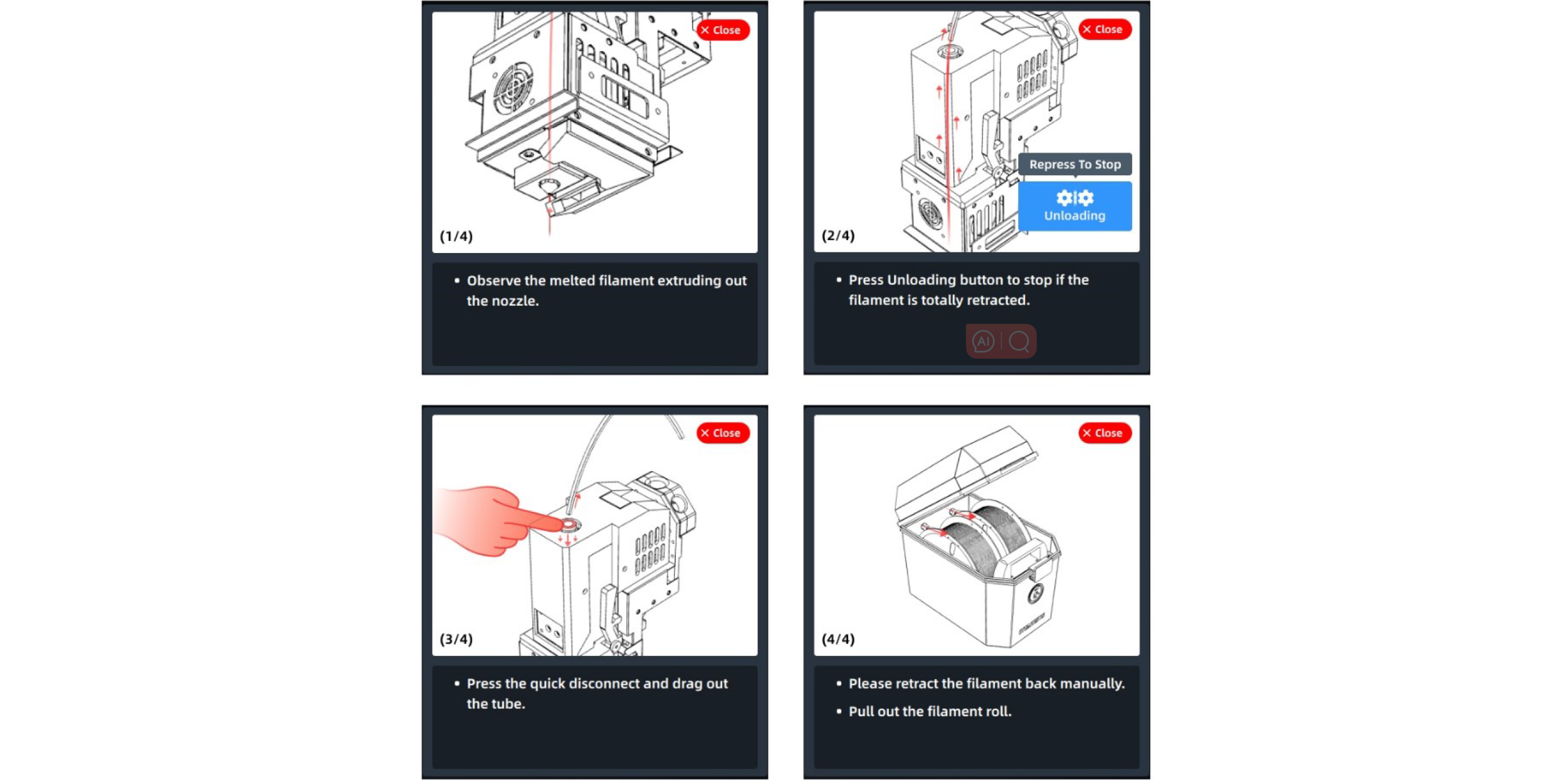
¶ 4.4.4 Supply Material after Out-of-material Alarm
The printer provides the out-of-material alarm function. When the filament runs out, the printer will pause while an alarm code prompting you to change the material will pop up on the screen.

Click the "Supply Filament" button on the screen, and then change the material according to the prompts on the screen. The procedure is as follows:
1. Unload old filament with reference to section 4.4.3 "Material Unloading".
2. Load new filament with reference to section 4.4.2 "Material Loading".
3. After the filament is loaded, click the "Print" button on the screen to continue printing.
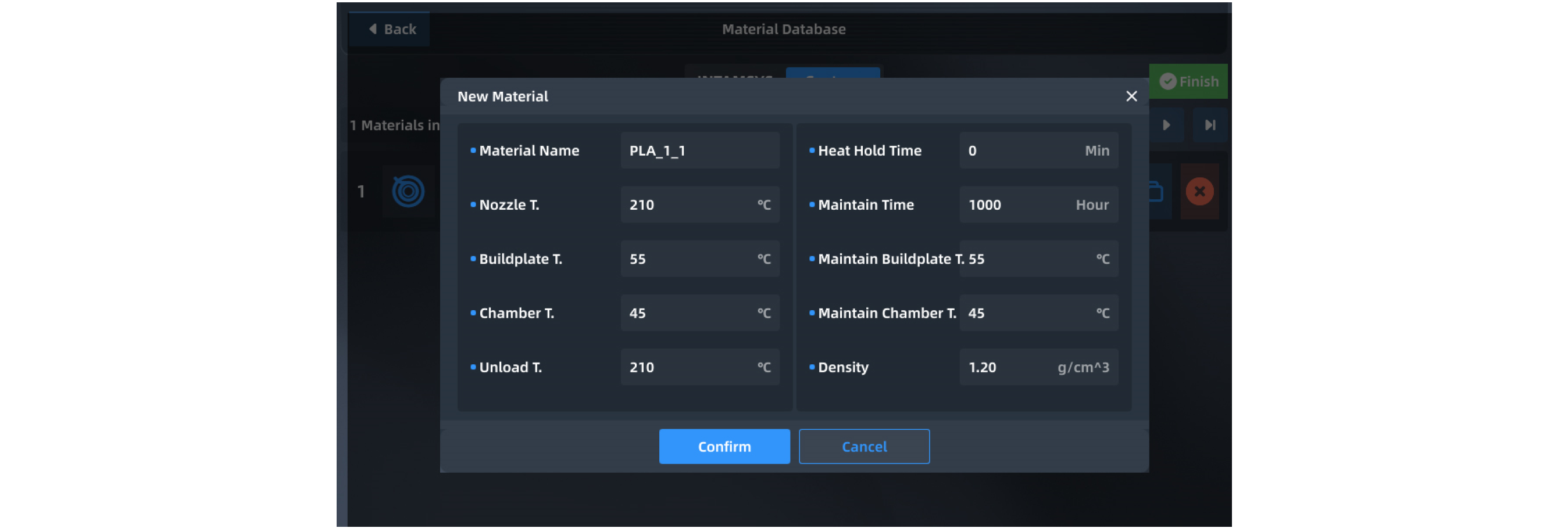
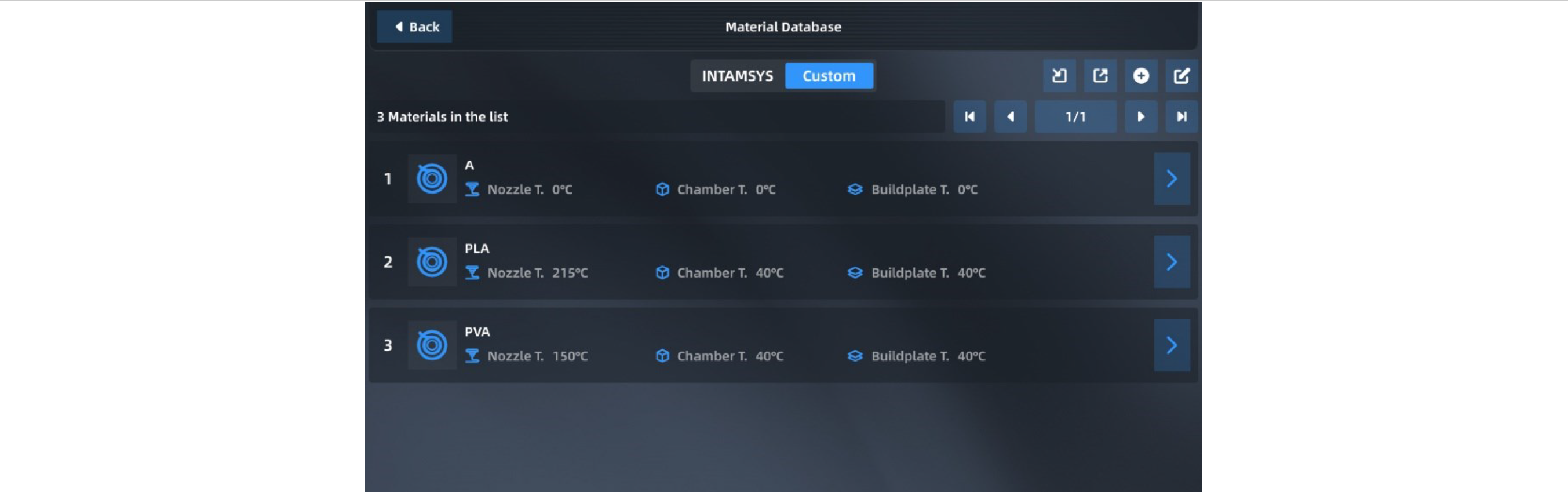
¶ 4.4.5 Material database management
| Press "Material Database" in the upper right corner of the material interface to enter the material database to view the details of built-in material attributes. The built-in material attributes of INTAMSYS cannot be modified or deleted, but its copy can be generated by clicking . After parameter modification and setting are completed, the new material process parameters will be stored in the user-defined materials. |
 |

| Note: These material process parameters are only used for printer operations except for formal printing. Such operations include material loading, material unloading, leveling, XY calibration, Z calibration, preheating, and heat hold, etc. During formal printing, the printer will run the parameters of the loaded G-code command file, instead of the preset parameters in the printer. | |
| In the user-defined interface, you can click the right icon to create a new material print process. Enter corresponding parameters and click OK to save. |
 |
| Click to modify, copy or delete the existing material process parameters, and click "Finish" to save the above operations. |
 |
| Click right 2 icons in the user-defined interface to export existing printing process parameters or import external parameters. Select the path to save or read parameters. It facilitates parameter transplantation. |
 |


¶ 4.5 Tools
The Tools page is divided into three functional modules: axis control, calibration and Tune.In Axis interface, you can adjust the positions of the nozzle and hotbed. In the Calibration interface, you can perform the printing build plate leveling and XY offset. In the Tune interface, you can adjust the parameters during printing.
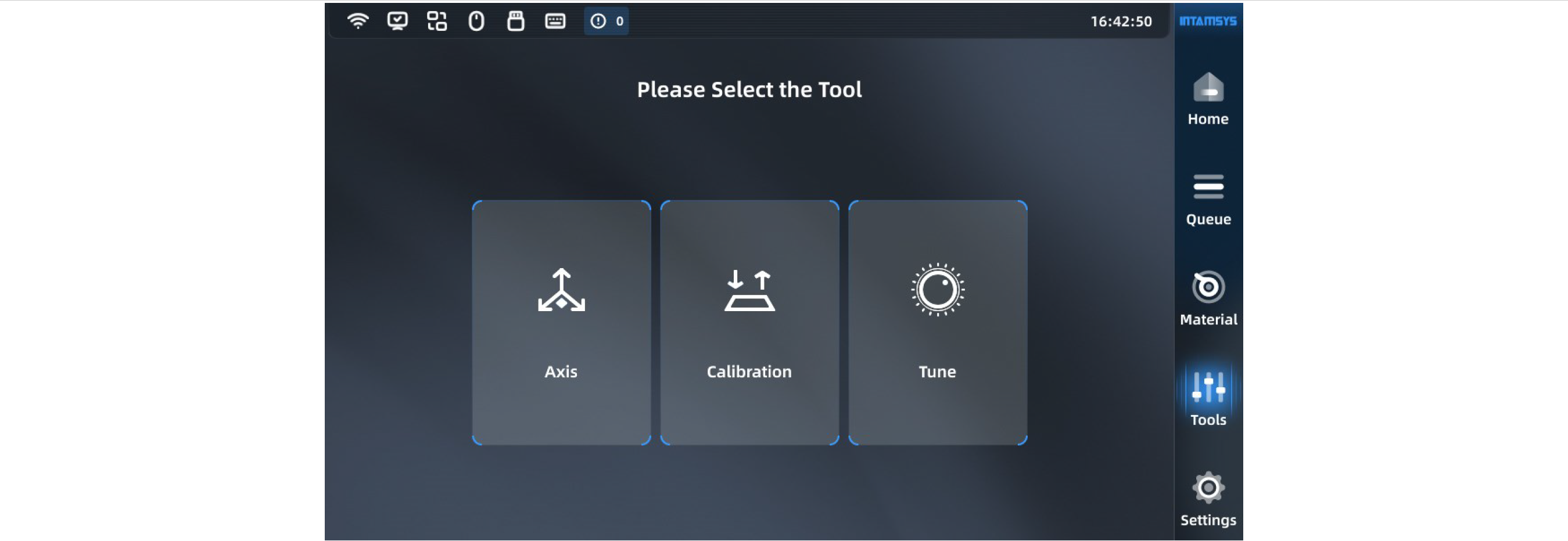
¶ 4.5.1 Axis control
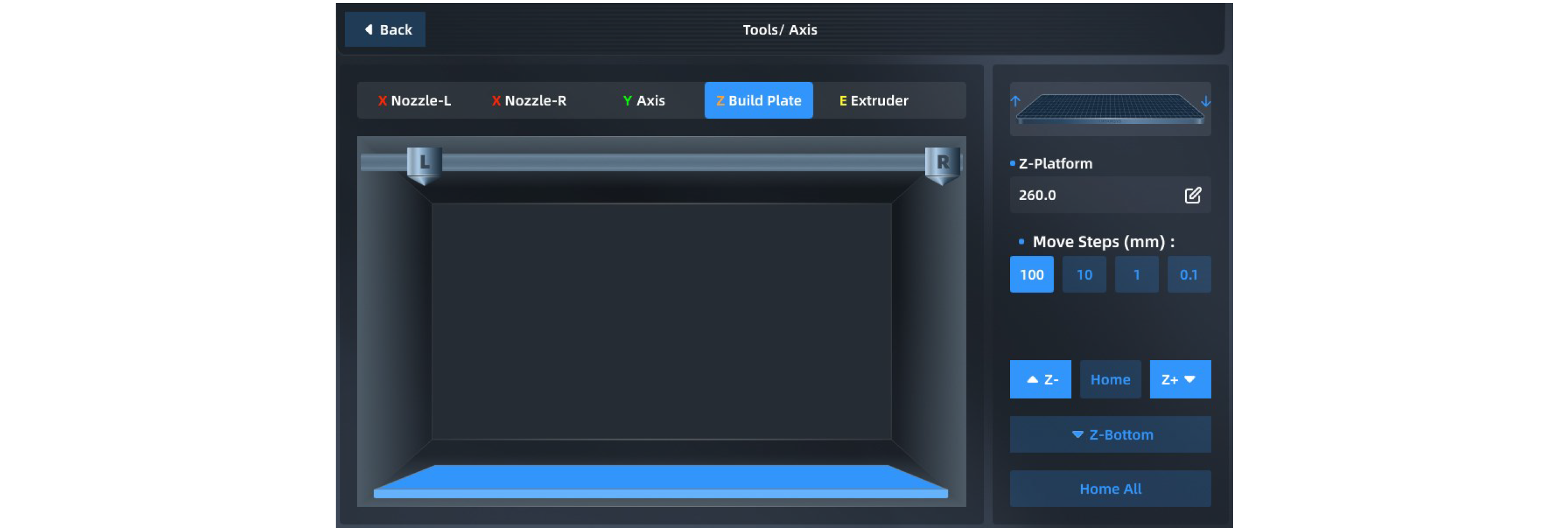
You can manually operate the position of the moving platform and printing nozzle in the Axis Control interface to control the material extrusion of the nozzle. Select the part to be operated at the top, click the arrow button at the bottom left to move the part, and adjust the moving step size. Click "Reset" to return the corresponding part to its original position. The position of the part will be updated synchronously in the left preview image during operation.
We can also enter the absolute value of position directly at the top right to move the part.
Axis Control > Left Nozzle interface:

Axis Control > Right Nozzle interface:
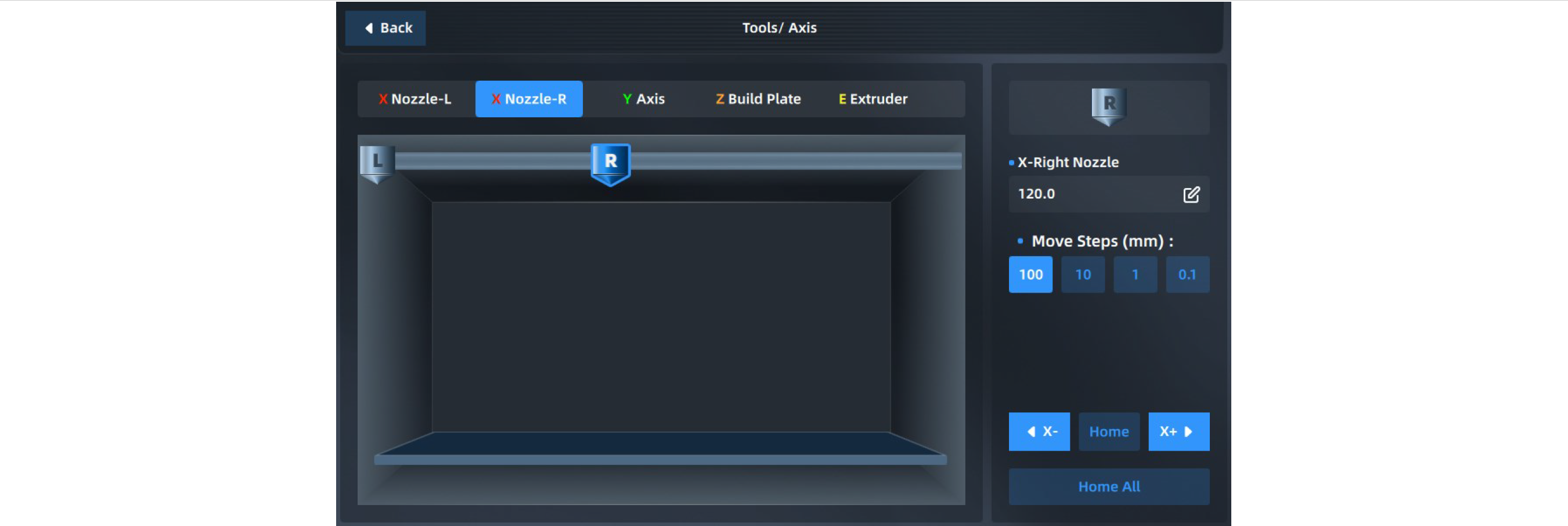
Y-axis Control interface:

Z-hotbed interface:
E extruder interface:

¶ 4.5.2 Calibration
Click the "Calibration" button in the Tools interface to enter the interface of printing build plate leveling and Nozzle XY Offset.
Printing build plate leveling: Use pressure sensors to automatically detect the distance between the nozzle and buildplate and the flatness of different positions of the buildplate
Nozzle XY Offset: Compensate for nozzle XY by printing standard samples.

You can choose to perform any one or several of these steps. When the printer is used for the first time, the calibration steps must be carried out in sequence. The following table guides you on how to selectively perform the steps after different operations. (●indicates this step is required, while — indicates this step is not required.)
Table 6.1 Conditions for Leveling and XYZ Calibration
| Conditions | Step 1: Leveling | Step 3: Nozzle XY offset |
| After replacement of L-Nozzle | ● | ● |
| After replacement of R-Nozzle | ● | ● |
| After replacing with a new print head assembly | ● | ● |
| After replacing with a new printing build plate | ● | — |
| Leveling error | ● | — |
| Nozzle XY Offset error | — | ● |
¶ 4.5.2.1 Calibration of automatic printing platform leveling
| 1. After the leveling function is enabled, the nozzle is automatically heated to the material temperature. After the nozzle temperature reaches the material temperature, spitting occurs and then the nozzle automatically drops to 150°C. |

|
| 2. Clean the nozzle, and then check "I have done it" in the interface selection box. |

|
| 3. After ticking "I have done it" in the interface selection box, the build plate is automatically heated to the required temperature for materials. |

|
4. After heating the buildplate, the interface automatically jumps to the automatic leveling interface. Select Simple (4*4) or Complete (10*10) mode for automatic leveling. By taking 100-point leveling as an example, click "Start Leveling", and the printer first performs a trigger test of the leveling sensor.

|

|
5. After the leveling sensor test is passed, the extruder will move to the center position on the front side of the platform for datum point test.
6. After the datum point test, start the 100-point leveling test. The printer automatically performs multi-point position leveling and records the error value of each point.

7. After the leveling process, you can click "Next" to start printing if the leveling is successful. During printing, the Z-axis position of the platform will be automatically compensated according to the movement of the extruder.
Note:
- During the installation of the printing build plate before leveling, it shall be correctly adsorbed on the platform along the guide grooves on both sides of the platform base plate;
- Clean the residual materials on the nozzle tip before leveling;
- Clean the printing platform before leveling; no foreign matters shall be left;
- Clean the chamber before leveling to prevent the platform being lowered from colliding with foreign matters;
| The screen displays the maximum and minimum values of all measuring points for leveling on the right side. When the difference between the maximum and minimum values is over 0.5 mm, leveling failure is prompted to request you to perform manual leveling as guided in the figure (refer to section 4.6.6). After manual leveling, return to this interface to perform automatic leveling again. |

|
| If automatic leveling exits and an alarm is given due to sensor failure during leveling, it is recommended to first perform manual leveling (refer to section 4.6.6), then manually conduct nozzle Z offset(refer to section 4.6.7), and finally disable the automatic leveling function in More Settings of the Settings interface before printing. |

|
¶ 4.5.2.2 Nozzle XY Offset
After automatic leveling or manual leveling and nozzle Z offset, start to conduct nozzle XY offset. Following the steps below, the machine reads XY offset of the L&R Nozzle through a printed scale for compensation during printing. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete the operation in turn.
1. Select nozzle XY Offset.

2. Make pre-calibration preparations as prompted.

3. Wait for the left and right nozzles and hotbed to be heated to the target temperature in sequence.

4. Start to print the calibration model, namely the scale.
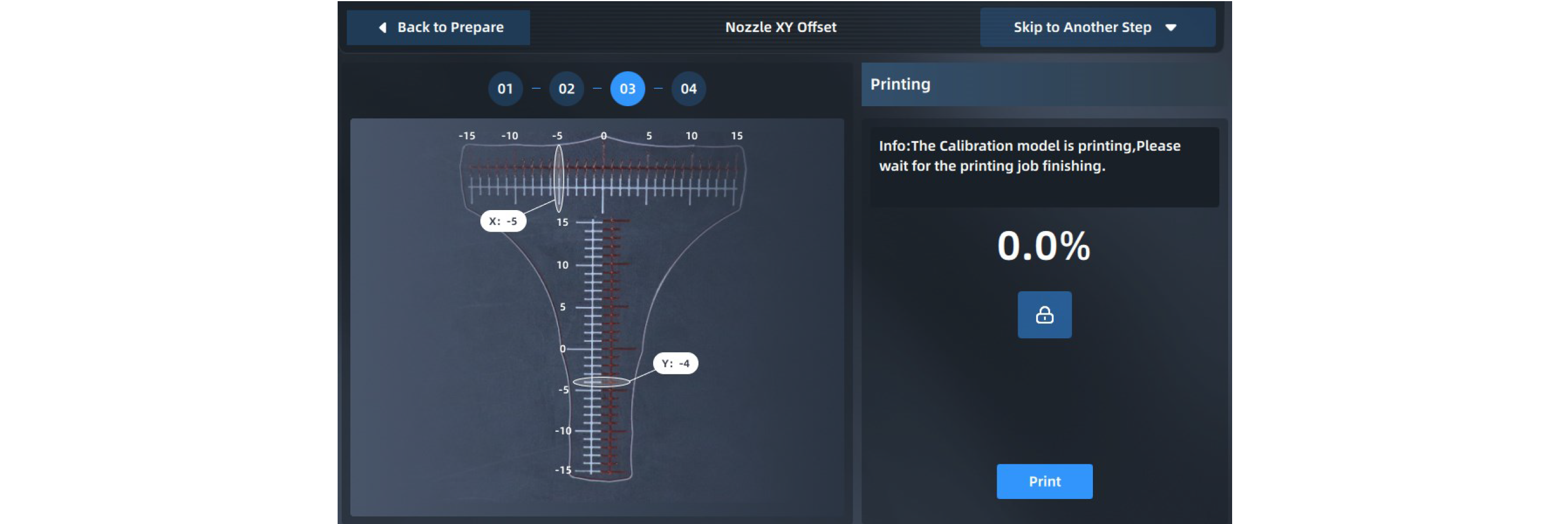
5. After printing the scale, take out the printing Build Plate to read the scale to obtain X offset value and Y offset value respectively, and click "+"/"-" buttons to enter values.
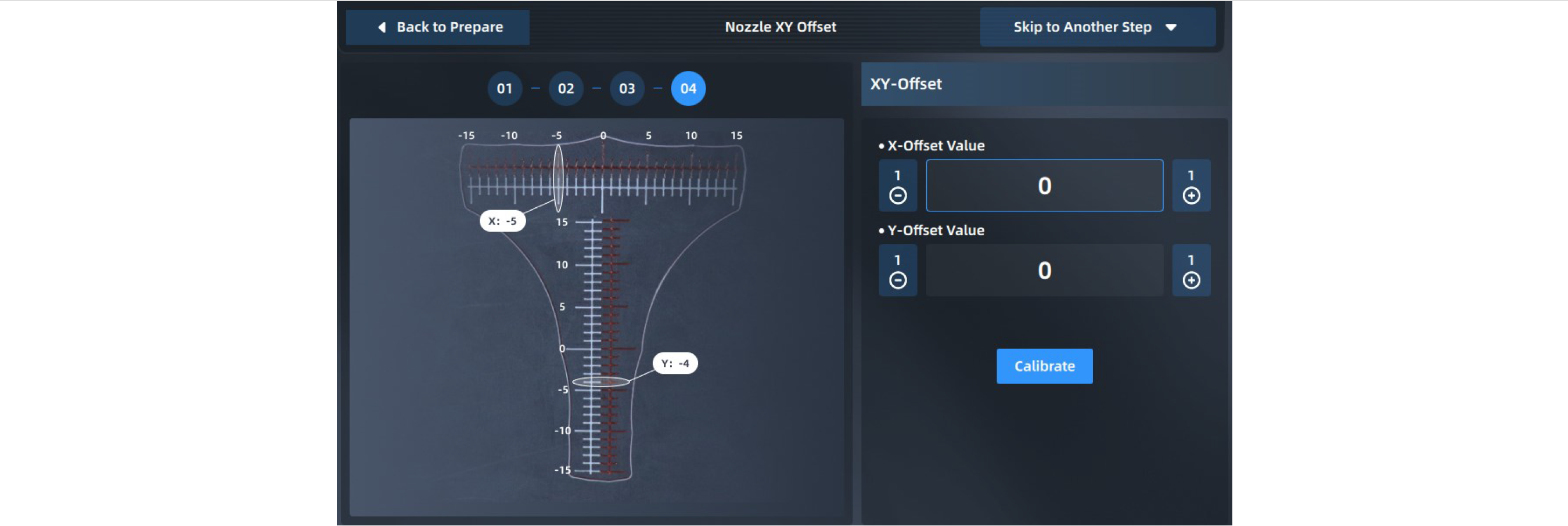
The scale shall be read as follows:
(1) Read the scale of the model printed by the right extruder based on the model printed by the left extruder;
(2) First, read the X offset value to check whether the center line of the model printed by the right extruder is to the left or right of the center line of the model printed by the left extruder. Use the "-" value for the left and the "+" value for the right;
(3) Then, read the Y offset value to check whether the center line of the model printed by the right extruder is above or below the center line of the model printed by the left extruder. Use the "-" value for below and the "+" value for above.
(4) Find the scale line where the two models are most aligned, then count from the center line to this scale line and record the value as N.
(5) Enter the "N" value into the input box. For example, the figure below shows the scales printed during an XY offset. The X offset value shall be "+6" and the Y offset value shall be "-5".
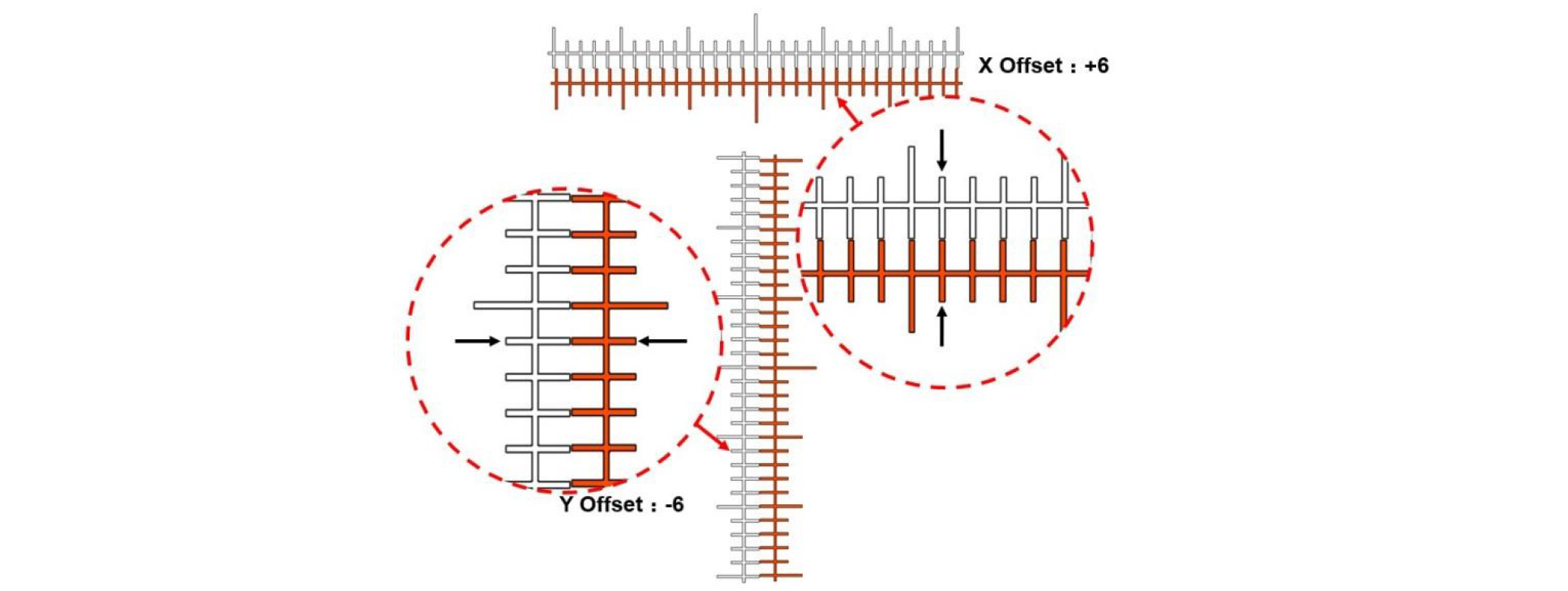
Note: The offset value 1 represents a scale, an actual deviation of 0.05 mm.
If it is found that the center lines for the horizontal or vertical print scale range are far apart and other scale lines are difficult to coincide with each other after reading the print scales, it means that the XY deviation has exceeded the measurable scale range (the maximum scale range is 15, that is, the deviation is 0.75mm). Take the following steps:
(1) First determine the offset direction "-"/"+" by observing the position of the center line of the model printed by the right extruder relative to the center line of the model printed by the left extruder;
(2) Set the offset to the maximum value, and click the "OK" button;
(3) Perform XY calibration again, print and test the models until a determined offset is read;
¶ 4.5.3 Tune
During printing, you can adjust the following parameters of the printer in the "Tools/Tune" interface: L-Nozzle T., R-Nozzle T., Chamber T., Hot Bed T., Left Fan Speed, Right Fan Speed, Print Speed and Material Flow.
The steps are as follows:
Click the icon of the parameter to be adjusted to highlight it.
Change the parameter value by clicking "-"/"+" on the right or turning the knob below, and the exact value will be displayed in the box.
Click the "Apply" button to complete parameter setting.

¶ 4.6 Settings
The Settings interface is used for relevant settings of the system, including device information viewing, software upgrade, networking setting and printer system parameter settings, etc.

¶ 4.6.1 Device Information
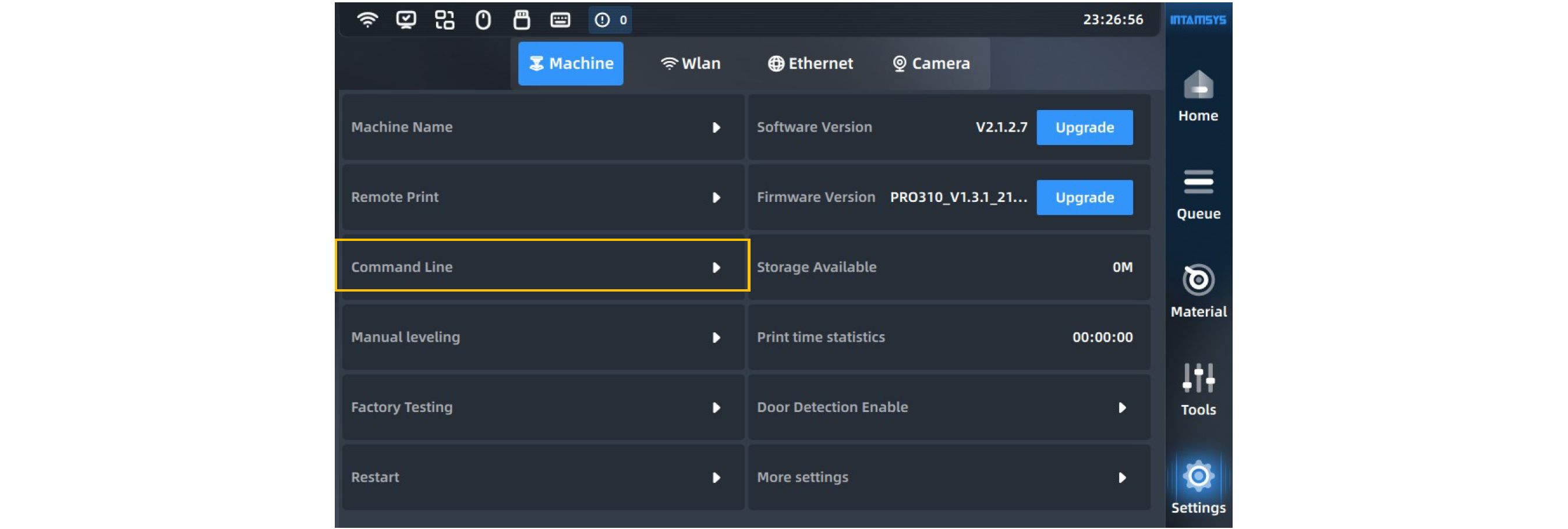
You can set the printer on this page, including:
- Machine Name: Set the printer name with alphabetic characters, special characters, and numeric characters (ASCII code).
- Remote Print: Set the remote print mode
- Command Line: Input the control device through command line
- Manual Leveling: Try to adjust the printing platform through manual leveling when automatic leveling fails
- Manual L&R Nozzle Z Offset: Manually calibrate the height difference between left and right extruders.
- Restart: The device automatically restarts.
- Software Version: Display the current software version number. To update it, click the "Update" button on the right
- Firmware Version: Display the current firmware version number. To update it, click "Update" on the right
- OS Version: Display the current system version number.
- Storage Available: Display the available memory of the current machine.
- Print Time Statistics: Display the total print time of the current machine.
- More Settings: Including screen brightness adjustment, automatic screensaver time, language switching, automatic time setting and motor and material shortage detection enabling (screen or LED brightness adjustment, automatic screensaver time, Wi-Fi auto reconnection, automatic leveling/motor/material shortage detection/door detection enabling, language, date and time, and restore factory settings)

¶ 4.6.2 Remote Print
In the Device Information interface, click the "Remote Print" button to enable remote print, and connect the printer to the computer through the IP address to support remote sending and print of G-code files. (Refer to section 5.4.3.2 for details)

¶ 4.6.3 Camera Settings
Set the camera parameters, and you can preview the video here.

¶ 4.6.4 Motor Enabling
The "Motor Enabled" switch is used to enable/disable X-axis motor, Y-axis motor, Z-axis motor, extruder motor, auxiliary feeding motor, etc.
Click "More Settings" in the Settings interface, and then click the button on the right side of the "Motor Enabled" to turn it On/Off. Blue indicates "On".
"On" means that all motors are powered on and "Off" means that all motors are powered off. After it is disabled, you can push each motor to move freely for easy maintenance.

¶ 4.6.5 Automatic Screensaver Settings
Click "More Settings" under the Settings interface, and then click "Screen save time" to set the automatic screen save time to 10 min to 30 min in a step of 10 min.

¶ 4.6.6 Manual Calibration of Printing Platform Leveling
For manual leveling, measure 4 points on the platform through a feeler gauge (thickness: 0.2 mm), while rotating the screws under the printing platform through an M8 screwdriver to keep the distance between nozzle tips of the 4 points and the hotbed platform consistent, so that the overall XY motion plane is parallel to the hotbed platform. Manual leveling is achieved only by the left nozzle.
1. After automatic leveling fails, enter the manual leveling interface as guided, or click "Manual Leveling" in the Settings interface and operate according to the pop-up prompts.


2. First tighten the screws counterclockwise one by one to slightly lower the hotbed.
3. Adjust the first screw in the left front corner, measure the distance between the nozzle and the printing platform with a feeler gauge (thickness: 0.2 mm), pull the feeler gauge back and forth until it just passes through, and then click the "Next" button;
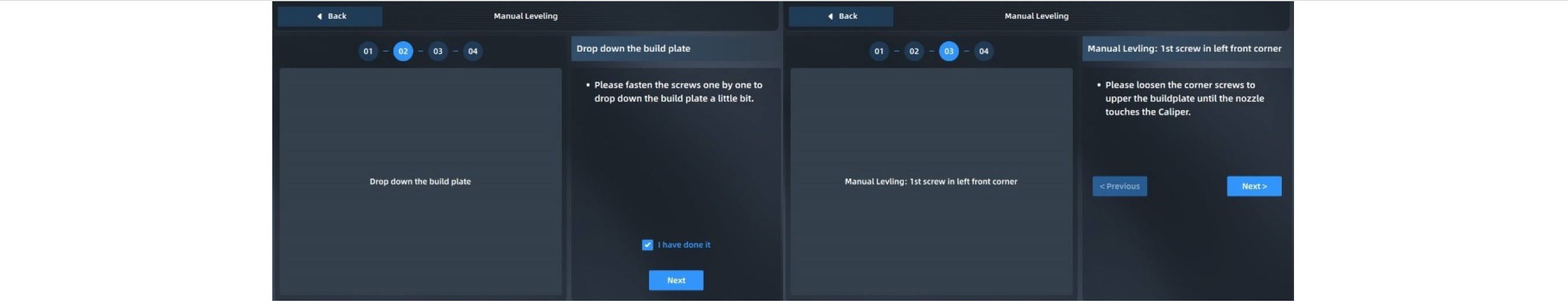
4. After adjusting the 4 points on the platform for the first time in the same way, check "I have done it", and then click "Next" to repeat the leveling;
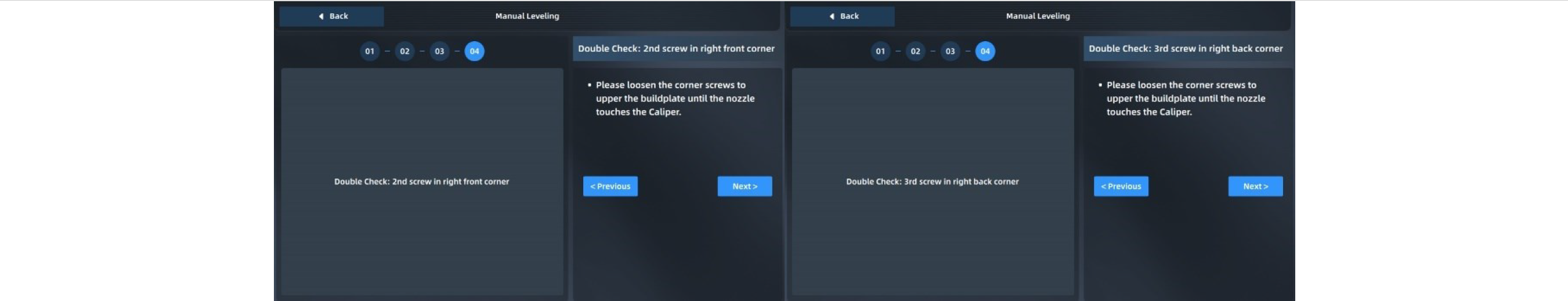
5. After the second manual leveling, a Complete button pops up on the screen. Click it to lower the platform to the bottom of Z-axis, and then return. Manual leveling ends.

Note:
- During the installation of the printing buildplate before leveling, it shall be correctly adsorbed on the platform along the guide grooves on both sides of the platform base plate;
- Clean the residual materials on the nozzle tip before leveling;
- Clean the printing platform before leveling; no foreign matters shall be left;
- Before leveling, clean the chamber to avoid collision with foreign matters when the platform descends.
¶ 4.6.7 Manual L&R Nozzle Z Offset
Test and manually calibrate the L&R Nozzle Z Offset through a 0.2 mm-thick feeler gauge.
(1) Enter from Settings, select "Manual L&R Nozzle Z Offset", and perform operations in turn according to the prompt on the screen.

(2) Prepare a 0.2 mm-thick feeler gauge to ensure that the hotbed platform is tightened without residual materials.

(3) After waiting for the left and right nozzles and hotbed platform to be heated to an appropriate temperature, clean up the materials adhered to the nozzles with an accompanying brush, and click "I have done it".

(4) Measure the distance between the nozzle and the printing platform with a feeler gauge (thickness: 0.2 mm), pull the feeler gauge back and forth until it just passes through, adjust the distance on the screen so that the nozzles rise or drop, and then click "Calibrate" button.

(5) After the L-Nozzle offset is completed, calibrate the R-Nozzle with the same method.

(6) The offset value of the heights of the left and right extruders is displayed in a pop-up window. Click "OK" to end Z-axis offset.

¶ 4.6.8 Wi-Fi Settings
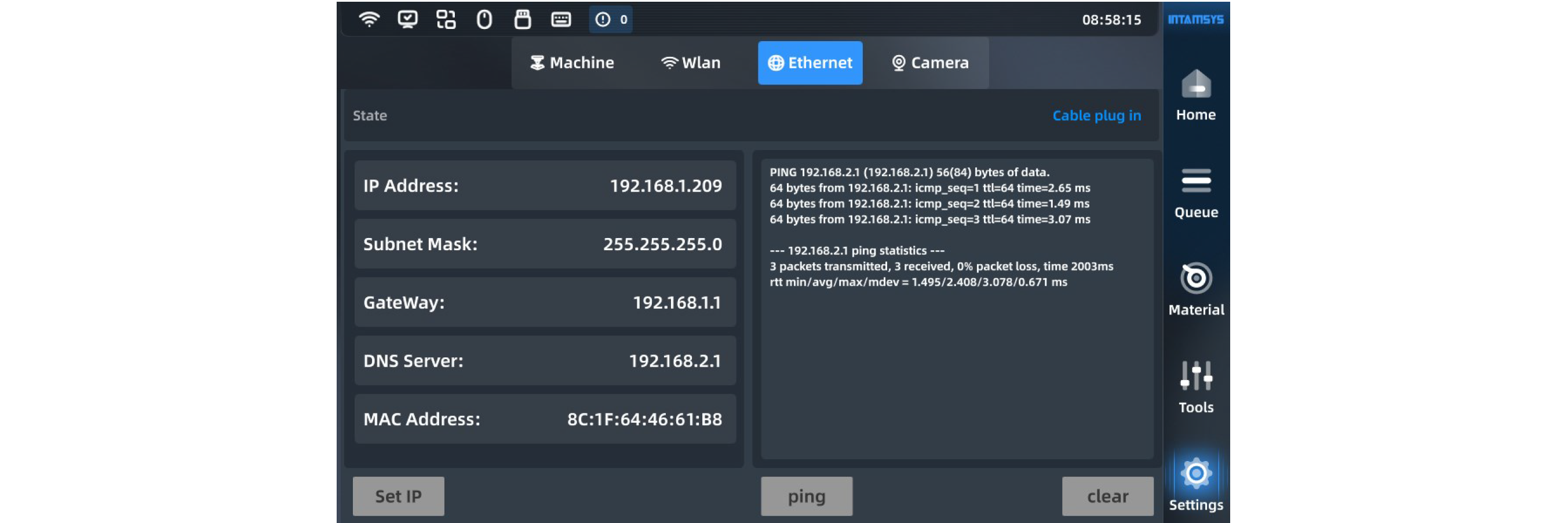
Wi-Fi connection can be enabled for the printer. Click "Settings" to enter the wireless network interface, and enable/disable it through the button on the right side of WLAN. Blue indicates that it is enabled. Wi-Fi connection can be enabled or disabled in the WLAN interface, which displays the Wi-Fi list on the left side. It can be automatically refreshed or refreshed after the user slides the screen. On the left side, select the Wi-Fi that can be connected and enter the password to connect with it. The device can automatically record the password and access the Internet. Enable DHCP mode, click the "Apply" button, and the machine automatically acquires the unmodifiable IP address and other contents. To manually modify the IP address and other contents, manually disable the DHCP mode to enter the manual setting mode, modify them, and click the "Apply" button to apply them. You can configure other Wi-Fi settings. After restart, the printer will automatically reconnect to the last Wi-Fi hotspot (on the premise that the following options are enabled: Settings Interface > More Settings > Wi-Fi Auto Reconnect.

¶ 4.6.9 Wired Network Settings
The printer can be connected to the Internet through a network cable. Click "Set IP" at the bottom left to complete the basic settings. Enable DHCP mode, click the "Apply" button, and the machine automatically acquires the unmodifiable IP address and other contents. To manually modify the IP address and other contents, manually disable the DHCP mode to enter the manual setting mode, modify them, and click the "Apply" button to apply them.
¶ 4.7 Other Interfaces
¶ 4.7.1 Warning Prompt
| The warning information icon can be displayed in the status bar at the top of the main interface. You can click to view the error code, and handle it according to the description and prompt operations to clear the warning. |
 |

You can view previous warning messages of the last day, last three days or last week.

¶ 4.7.2 Resume print
If we get some error messages during printing, indicating that print can be resumed. You can operate by simply following the steps in the wizard.
¶ 4.7.3 Command line
Command line refers to the mode in which the printer is open to developers. It is mainly used for debugging and fault diagnosis of the printer and does not need to be enabled during normal printing. In command line, the printer can be controlled and fault diagnosis can be conducted by sending G-code.
You can enter "Command Line" through Settings interface.
¶ 5 Operate Printer
This chapter describes the basic operational steps for operating FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO.
¶ 5.1 Startup and Shutdown of Device
¶ 5.1.1 Power on the printer
1. The power socket is located on the lower right side of the machine. Connect the two ends of the power cord to the AC power supply plug (printer voltage: 110V and 220V) and the power socket of the printer, respectively;
2. Insert the power plug, then switch the power switch next to the power socket of the printer to the (I) position;
3. Turn on the front ON/OFF button on the right side of the screen in the front of the printer, and the button indicator is on. At the same time, operate the screen to enter the start interface, and the printer starts.

¶ 5.1.2 Power off the printer
Press the power button (which is also used to turn on the printer) on the front side of the printer. Note: This operation is only to turn off the printer. To power off the printer, the power switch must be switched to the (O) position.
Note: If the printer is not in use for a long time, disconnect the power cord from the AC power supply socket.
¶ 5.2 Preparation of Print Materials
This section guides you on how to load filaments into nozzles. When completing the required steps, be sure to follow the operation prompts displayed on the touch screen. The printer is supplied with an independent filament box (INTAMBox) that can hold up to two rolls of 1 kg material. The left compartment is used for printing by the left extruder, mainly for model materials, and the right compartment is used for printing by the right extruder, mainly for supporting materials.
Note: Make sure that there are no print parts or other debris on the printing platform when loading or unloading filaments. Because the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis will be reset during this operation, and any print parts or other debris on the printing platform can collide with the extruder or X beam.
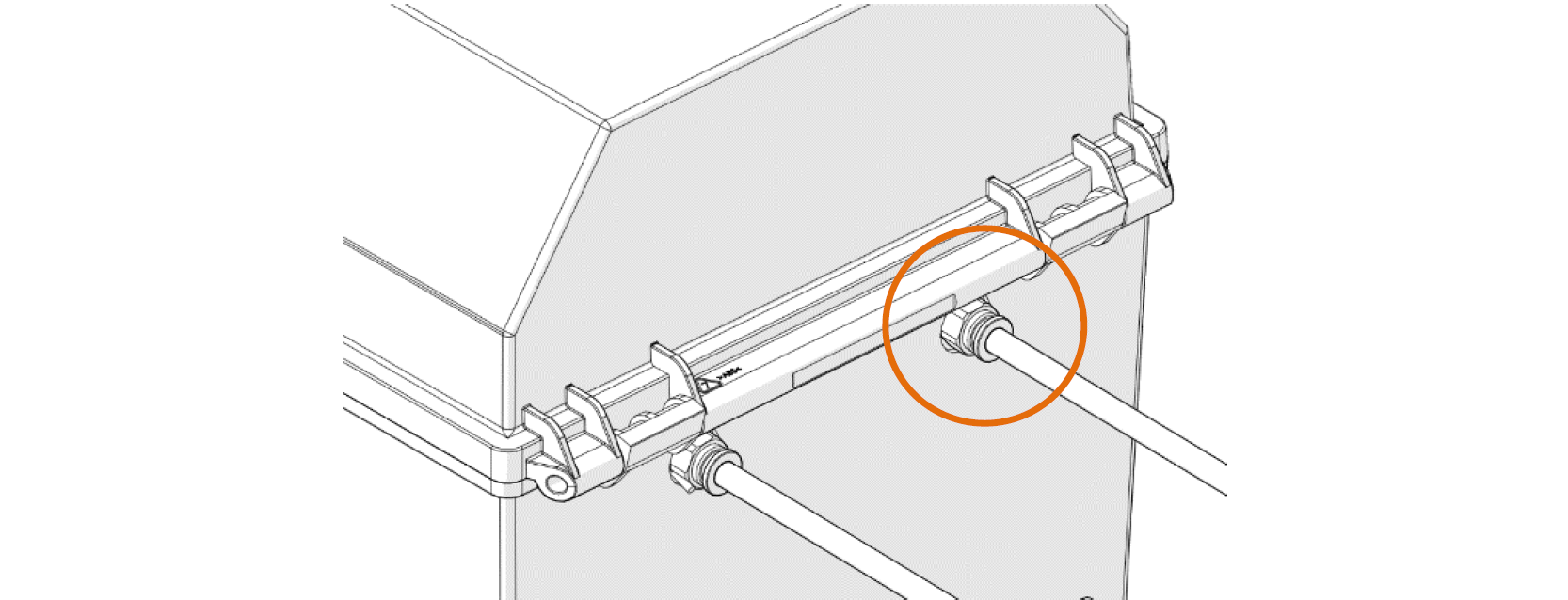
1. The filament box is placed on the right side of the printer, as shown in the figure. Insert one end of the feeding pipe in the accompanying accessories of the filament box into the quick connector and the other end into the quick connector located on the right side of the printer. The feeding pipe should be inserted to the bottom for smooth feeding.
2. Unbuckle the upper cover of the filament box, place the drying box in the front slot of the filament box, put the wire rod on the roller of the filament box as shown in the figure, and then thread the wire rod through the quick connector at the rear end until the material protrudes from the feeding pipe of the printer. After manual loading is completed, buckle the upper cover.

3. Click the "Material" button on the screen operation interface, click the left or right wire coil icon to select the extruder to be loaded with materials. The highlighted icon indicates the extruder is activated;

4. Pressing the "Material Name List" button will display INTAMSYS materials and user-defined materials. Materials that we used recently and frequently will be at the top, where we can scroll down to select available materials. User-defined materials can be configured in the material database.

Specifically, if the material on the printer is inconsistent with the material settings in the G-code print file, the system will alert the user to check the material. Click "Apply". Then the material will be automatically applied to the L&R Nozzle.
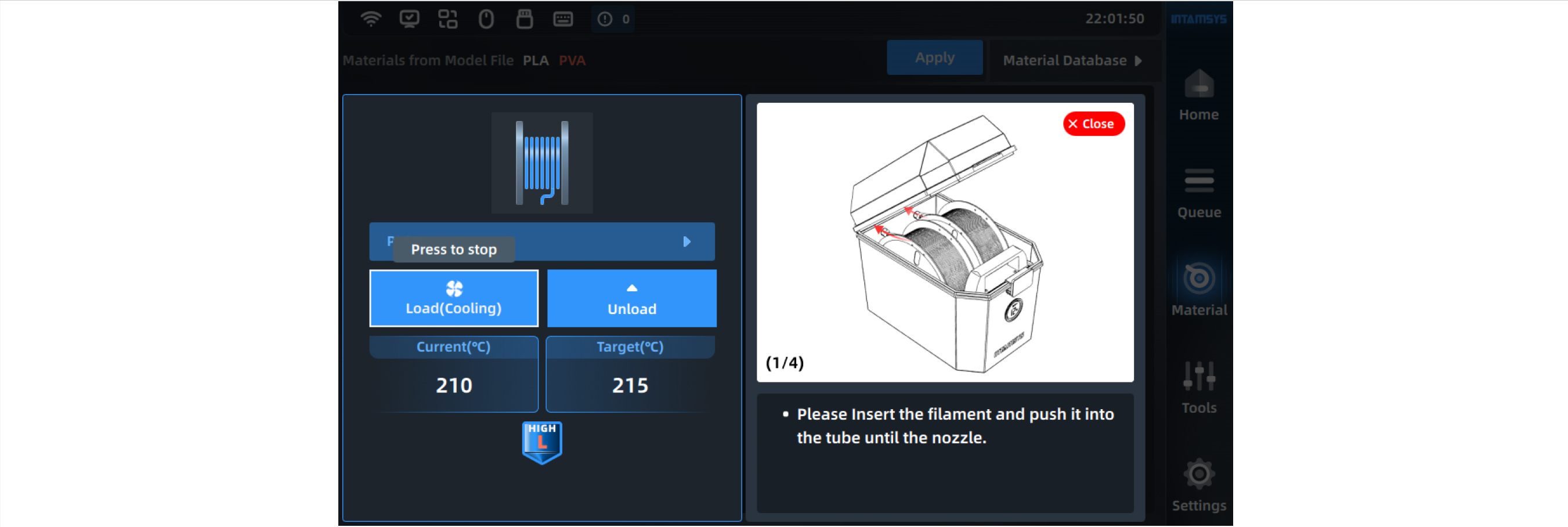
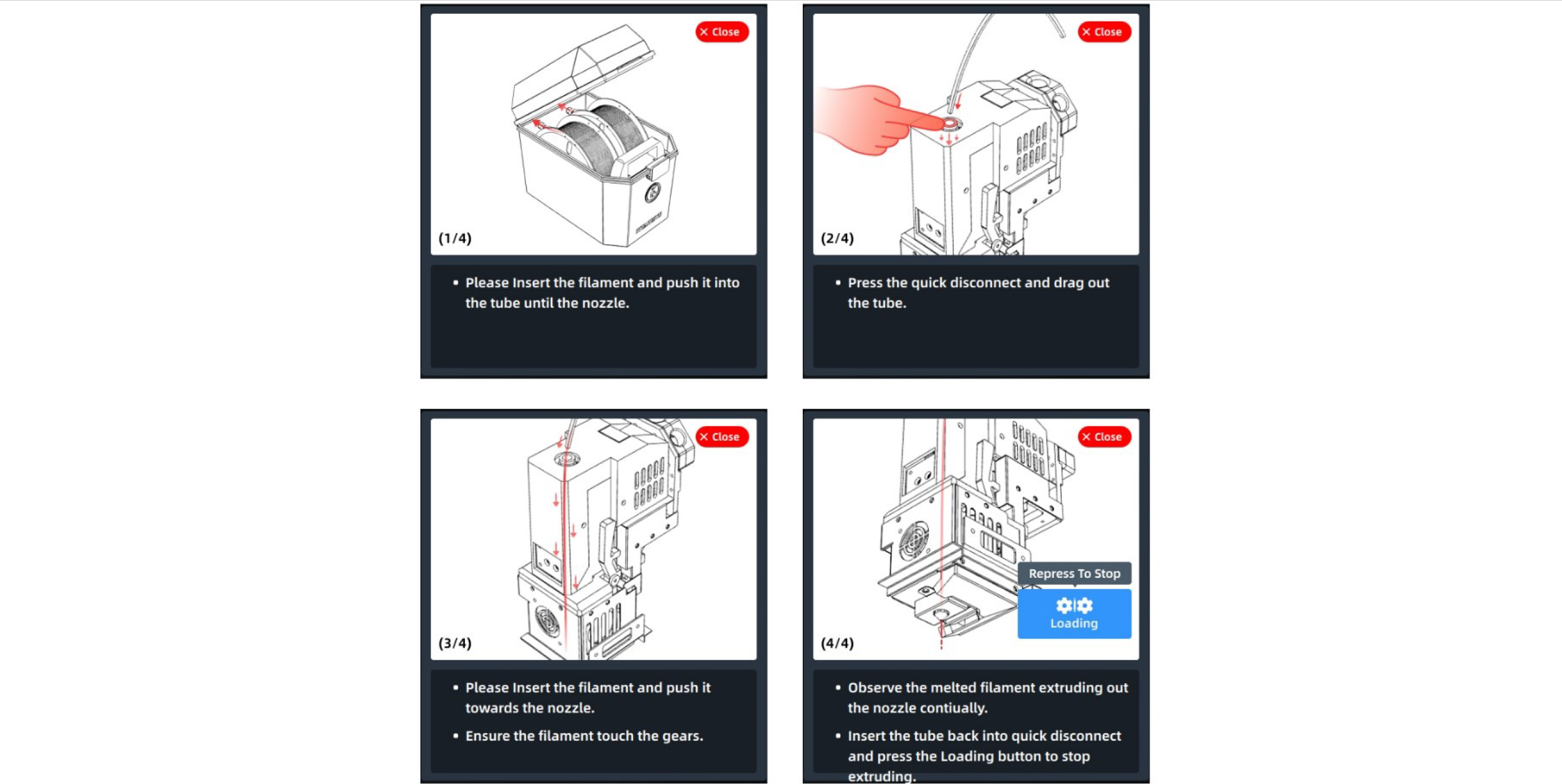
5. After selecting the material, press the Load button to load the material step by step according to the pop-up wizard.
- After heating the nozzle to the target temperature, we can prepare materials according to the prompts on the right;
- The user can click the "Stop Load" button or other blank areas to exit the loading process;
- The user can close the prompt window, which will be collapsed for later viewing.
Please refer to 4.4 "Materials" for operations such as material unloading, material process template modification and material database modification.
¶ 5.3 Nozzle Replacement and Material Change
There are two types of printing nozzles: The integrated silver-white nozzle is made of CuCrZr and can print all materials except fiber-containing materials (PA6-CF/PA12-CF, etc.), such as ABS+, ABS-HS, ASA, HIPS, PA6/66, PC, PC/ABS, PC-FR, PC-PBT, PLA, PVA, SP3030, TPU-95A, PETG, PPS; the combined silver-white nozzle is mainly made of CuCrZr and high-hardened steel at the tip and mainly prints fiber-containing materials, such as PA6-CF/PA12-CFPET-CF, PET-GF, PPA-CF/GF, PPS-CF/GF, SP3050, and SP5010.
It is strongly recommended that one nozzle prints only one material, which is conducive to stable operation of the device and easy management.

¶ 5.3.1 Replace the Nozzle
The procedure of nozzle replacement is as follows:
1. Click the "Material" button on the main interface to enter the Material interface.
2. If there is still material in the nozzle, click the "Unload" button first to unload the filament according to the prompts.
3. Click "Target Temperature" and set it to the extrusion temperature of the material. After confirmation, the nozzle will be automatically heated to the target temperature. Remove the nozzle with a 7 mm socket wrench.
4. Take out the high-temperature nozzle in the socket with tweezers, replace it with a new one and install it on the extruder.
5. After replacing the nozzle, hotbed leveling, XY offset are recommended.
¶ 5.3.2 Change Material before Printing
To change material type before printing, you shall not only change the material on the Material interface, but also selectively replace the printing nozzle. Different nozzles shall be used to print different materials. If you want to use one nozzle to print different materials, the nozzle temperatures for printing of such materials must be very close, and an extrusion temperature difference of no more than 50℃ is recommended.
Note: Do not use nozzles for printing overhigh melting point materials to print low melting point materials. For example, printing PLA with nozzles that have already printed PC will cause blockage of the extruder and printing failure.
- If the old and new material types are consistent or the nozzle temperatures for printing of different materials are close, it is not necessary to replace the nozzle. The procedure is as follows:
1. Unload the old material.
2. Select the new material to be loaded, and preform the loading operations.
- If the old and new material types are inconsistent or there is a big difference between the nozzle temperatures for printing of different materials, the nozzles shall be replaced; accordingly, leveling and XY offset shall also be done. The procedure is as follows:
1. Unload the old material.
2. Replace the nozzle.
3. Select the new material to be loaded, and preform the loading operations.
4. Perform again the step of hotbed leveling and XY offset.
¶ 5.3.3 Pause to Change Material
If you need to change material while the printer is printing, follow these procedures:
1. Click the "Pause" button at the bottom of the main interface and wait until the movement of the extruder stops completely.
2. Unload the old material.
3. Load the new material.
4. After the material is loaded, click the "Start" button on the lower part of the interface to continue printing.


¶ 5.4 Basic Printing and Operations
¶ 5.4.1 Prepare the Printer
Prepare the printer for printing:
1. Power on the printer (refer to section 5.1.1 for details);
2. Use an extruder brush to remove materials left on the extruder;
3. Clean the residues or impurities on the printing Build Plate and magnetic platform base plate;
4. Place the printing buildplate on the platform base plate along the left and right guide grooves of the magnetic platform base plate;
Note: The magnetic platform base plate has a large suction force. When placing, hold the printing platform handle tightly with both hands, tilt the printing buildplate, let it to contact the magnetic base plate on the rear side first, and then slowly lay it on the platform by magnetic attraction to avoid hand pinching.
5. Load materials according to the print task requirements.
6. Perform leveling and extruder XY offset. This step can be skipped if leveling and calibration have been done.
7. When ready, the printer can perform print tasks formally.
¶ 5.4.2 File Slicing
If G-code is unavailable, you can slice the file using INTAMSUITE NEO. If G-code is available, skip this step.
1. Download: Through the official website at https://www.intamsys.cn/ download the slicing software INTAMSUITE NEO
2. Import Model: Create a new project and import the model in the format of .stl, .step, .obj, .x3d, .oltp, .stp, .iges, or other intermediate CAD files.

3. Model operation: Right-click"Arrange All Models" to arrange all models and move them to the center of the printing platform.

4. Print settings: Select the printer model (select FUNAMT PRO 310 NEO here), and click the "Print Mode" command to select the print mode. FUNAMT PRO 310 NEO provides mirror print and copy print.

Select the material and nozzle diameter required for the print head. For double-head print, switch to the extruder 02. After selecting the material for the extruder 01, proper supporting material can be automatically recommended for selection.

The slicing software is pre-configured with various print profile templates, which can be selected as required, with the required process parameters adjusted in the detailed settings dialog box before slicing.

5. Print preview: Wait for slicing to be completed. After the operation is done, you can preview the slicing results by clicking "Preview" to view the print path and direction on each layer. You can even simulate the whole print process after checking the material color, line type, feeding speed, temperature, fan speed, and layer thickness in detail.

6. File saving: When you are satisfied with the previewed slicing results and save the print file to your defined location, the software will save g-code or ifp print file for direct remote print. You can also save it in the U-disk and later insert the disk to the printer for selective file printing or send it to the printer remotely. Refer to the following text for the operation mode.
Note: As the naming format for .gcode file is imported into the U-disk, names with Chinese characters or special characters are not supported for now.
For more detailed function operation of the slicing software, refer to:
https://help.intamsys.com/zh/home/INTAMSUITE_NEO/New_User_Guide
¶ 5.4.3 Import the Print File to the Printer
1. Select the location of the print file. Select the location where the file is stored in the drop-down bar in the upper right corner of the screen, such as USB storage or local storage (for remote print).
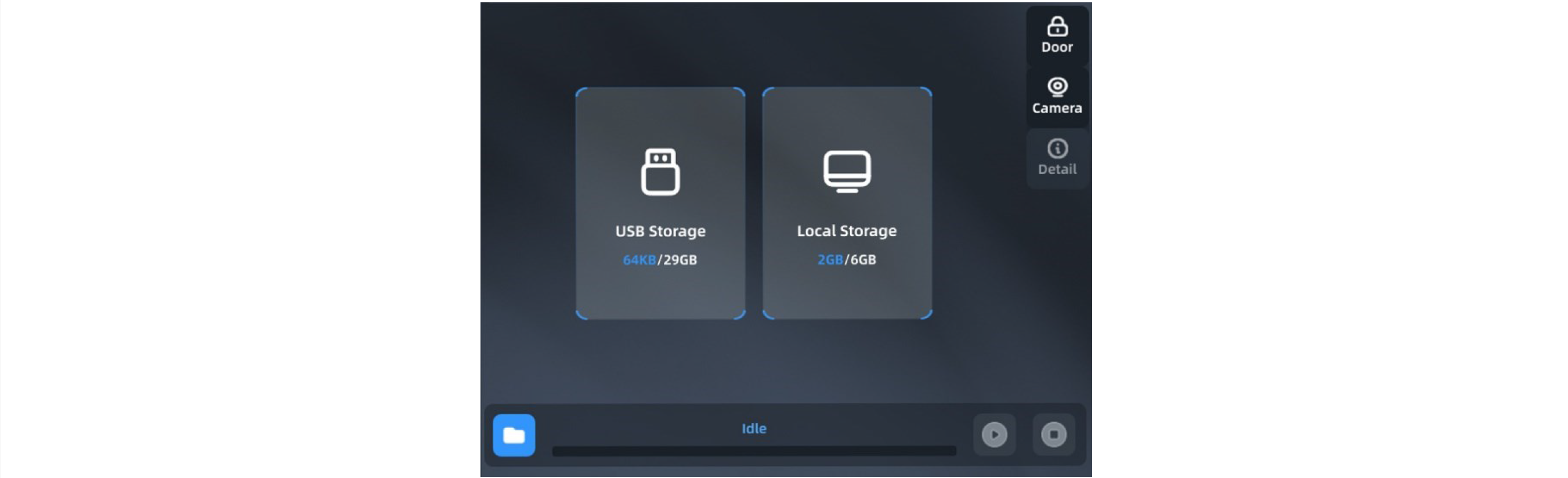
2. Click the Open icon in the lower left corner of the screen, and the print file list will pop up;

3. Select the print file, and click the "Print" button to load the print file. You can also select "Add to Queue" to add print files to the print queue. If you import the file through U-disk, after the print file is loaded, you can pull the U-disk out of the USB port without affecting the printing.
¶ 5.4.3.2 Remote Print
In the device information interface, click the "Remote Print" button to enable remote print and select the IP address on this page. You can view the log after connection.

Click "Remote Print Enabled", click the "IP Address", and select the IP address for remote connection of the device. The remote connection password will be displayed on the right side. Click "Refresh" to randomly change the remote connection password. When the "Server State" is displayed as "ON", the device has remotely connected for remote print.

There are three modes for remote operation. Before remote print, make sure that both the printer and computer work on the same LAN and the printer is remotely connected with the computer through IP address.
1. FTP transfer mode:
(1) Enter the IP address of the printer's remote client in the local Windows folder.

(2) Enter "root" as the username and "intamsys" as the password in the prompted dialog box to log in to the printer.

(3) Import the file to be printed to the .gcode folder, and the printer receives the uploaded file and prints the local file selected on its screen.

2. Remote print with INTAMSUITE NEO
(1) Install and open the computer software INTAMSUITE NEO
(2) In the toolbar interface, select "Print".

(3) Click "Add Printer" and select SFTP or FTP as the "Type IP Address". You can also click the "Search & Select" button to search for the IP address.

(4) Enter the IP address and remote connection password of the current printer, and click "Connect" to create a connection.
(5) Click "Upload File", and select the local file or the file of the slicing software.

(6) Click "Get to Print" to directly print the file on the slicing software or on the printer as it would also receive the print file.

(7) Start the G-code print task remotely, and the display screen of the printer will enter the print interface accordingly. For other remote operations, the screen interface will also display corresponding actions.
3. INTAMSUITE Local Print
Besides application in INTAMSUITE NEO, remote print can also be independently applied after starting the program named INTAMSUITE Local Print (installed together with INTAMSUITE NEO).
The INTAMSUITE Local Print tool is not disturbed by many slicing-related functions. It has a user-friendly interface for ease of operation.
Download the INTAMSUITE Local Print tool (Fig.5.31) and connect it to the printer through the IP address. You only need to select the print file to print in the same operation mode as that for remote print with INTAMSUITE NEO. For detailed steps, refer to: https://help.intamsys.com/zh/home/INTAMSUITE_NEO/Remote_Print

¶ 5.4.4 Printing Process
¶ 5.4.4.1 Main Printing Process
Click the "Start" button on the screen to start printing. If remote print is conducted through INTAMSUITE NEO or INTAMSUITE Local Print, manual operation is not required. The printing process has three steps: "preheat - print - heat preservation":
1. Preheat. Preheat the printing platform and the chamber before printing. The preheating temperature and time are the platform temperature, chamber temperature and preheating time of the material in the left extruder on the printer (it is necessary to confirm whether the material setting of the material interface is consistent with G-code). When the platform temperature and chamber temperature reach the target values, preheating timer starts;
2. Print. After the preheating time lapses, the printer starts to read the G-code file to perform formal printing.
3. Preserve the heat. After printing, the nozzle cools down and the printing platform and chamber shall maintain heated. The heat preservation temperature and time are based on the platform heat preservation temperature, chamber heat preservation temperature and heat preservation time of the material in the left extruder.
¶ 5.4.4.2 Modification of Preheating Time and Heat Preservation Time
During the printing process, you can modify the preheating time and heat preservation time.
1. Click the "Heat Preservation Time" button on the right side of the main interface to display the modification interface of preheating time and heat preservation time.
2. You can enable or disable "Heat Hold" and "Maintain" options.
3. Modify the time by clicking "-"/"+", and click the "OK" button to save the modification.
Note: Preheating and heat preservation need to be set before printing, and the settings during printing will not take effect; preheating can only be disabled or preheating time can be reduced when the heat preservation of chamber has been maintained for a long time, otherwise it will affect the next printing effect.

¶ 5.4.5 Duplicate/Mirror Print
FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO supports single-extruder print/regular dual-extruder print/duplicate print/mirror print.
Single-extruder print: Perform printing with an extruder at a time.
Regular dual-extruder print: Perform printing with two extruders in turn, one for model printing and the other for auxiliary structure or support.
Duplicate print: It means that a printer with dual independent extruders can print two models with identical dimensions, angle, and direction at the same time during 3D printing to improve the production efficiency. Copy print is very useful for the mass production of the same components or objects, significantly improving efficiency. Copy operation only needs to be performed for the existing model in the slicing software.

Mirror print: It means that a printer with dual independent extruders can print two symmetrical models at the same time during 3D printing. Through mirror print, the redesign of a symmetrical model can be avoided, and mirror operation only needs to be performed for the existing model in the slicing software.

The duplicate/mirror print is as follows:
1. Import the model file and select duplicate/mirror print.

2. According to individual print requirements, set the print parameters such as extruder and process template for the model, and preview slicing.

3. Transfer the sliced file to the machine which shall meet the following conditions at this point:
(1) Ensure the same print materials or similar process parameters for dual left and right extruders for duplicate/mirror print.
(2) Perform manual calibration of L&R nozzle Z offset before copy/mirror print.
If the difference between the left extruder offset and the right extruder offset is less than or equal to 0.2 mm, it means that the printer can directly perform duplicate print or mirror print; however if it is greater than 0.2 mm, you need to manually adjust L&R nozzle height and manually calibrate L&R nozzle Z offset, test and calibrate it with a 0.2 mm-thick feeler gauge, and perform operations as prompted on the screen in turn with reference to 4.6.7.

Note: For mirror/duplicate print, do not disable the raft layer settings. You only need to set mirror print in the slicing software (the raft layer is printed by default) and directly print the required file by sending the file remotely or inserting the Udisk.
¶ 5.4.6 Continue Printing
¶ 5.4.6.1 Continue Printing after Material Shortage
When the printer detects that the printing wire rod is used up, it pauses printing and continues printing after material reloading. This technology is very useful especially for long-term or large-scale printing tasks as it can prevent print failure due to materials useup during printing, with the operation steps as follows:
Click the "Supply Filament" button on the screen, and then change the material according to the prompts on the screen. The procedure is as follows:
1. Unload the old material.
2. Load the new material.
3. After the material is loaded, click the "Print" button on the screen to continue printing.
¶ 5.4.6.2 Continue Printing after Power Failure
In the case of power failure or other interruptions during printing, the function of continuing printing after power failure records the printer status at the time of power failure and prompts whether to continue printing after the device is powered on again.
This technology is particularly important for long-term important printing tasks as it can prevent print failure due to power failure in the midway and reduce energy and material waste, with the operation steps as follows:
1. Power on the machine after power failure during printing, and click "Clear" or "Close" for the 406 alarm displayed in the interface.

2. The prompt window of continuing printing after power failure pops up. Click "OK", an the machine reads the last printing progress and recovery temperature and automatically opens and continues printing the print file before power failure; click "Cancel", and the machine does not continue printing after power failure.

3. The machine starts to resume printing.
Note: Continuing printing after power failure poses the failure risk as the device is incapable of heating to make the Build Plate temperature and chamber temperature drop quickly after power failure and the model can be separated from the buildplate after longterm power failure. Therefore, the function can be applied within 10 mins after power failure.
¶ 5.4.7 Pause Printing
During printing, the Pause button on the main interface is activated. The printer can automatically pause or you can use this button to manually pause it.
¶ 5.4.7.1 Automatic Pause
1. When a red alarm is detected, the breathing light turns red and an automatic pause command is sent.
2. The Z-axis platform is slightly lowered, then the extruder resets to the zero position, the heating of the nozzle stops while an alarm dialog box pops up, indicating the reason for pause.
3. You need to correct the corresponding error first, then click the "Clear" button to clear the alarm.
4. To restore printing, press the "Start" button on the main interface, and a restoration command will be sent to the printer to instruct it to restore printing.
¶ 5.4.7.2 Manual Pause
1. Click the "Pause" button to manually pause the printer.
2. The Z-axis platform is slightly lowered, then the extruder resets to the zero position, and the heating of the nozzle stops.
3. To restore printing, press the "Start" button on the main interface, and a restoration command will be sent to the printer to instruct it to restore printing.
¶ 5.4.8 Stop Printing
After a print task is started, the "Stop" button in the main interface is activated. The printer can automatically stop or you can use this button to manually stop it:
¶ 5.4.8.1 Automatic Stop
When a red alarm is detected, the printer will automatically stop. After the printer receives the stop command, the heating of nozzle, platform and chamber will be disabled.
¶ 5.4.8.2 Manual Stop
When the printer receives the stop command, a dialog box for confirming or canceling the stop will pop up. Press "OK" to stop the printer. After the printer receives the stop command, the heating of nozzle, platform and chamber will be disabled.
¶ 5.4.9 Printing Alarm
If the printer detects a fault that might affect the printing, a warning will be given on the screen. The alarm status button will turn red according to the warning severity.
When you press the alarm status button, a dialog box that indicates the alarm reason will pop up. The dialog box shows information about the alarm reason.

In some cases, the alarm will prevent your attempted start to print, and the printing will not start until you eliminate the error. Various warnings might be displayed when the printer performs print tasks, and some warnings will pause and stop printing. Whether the printing process can be restored depends on the warning severity. Refer to Chapter 7 for the fault alarm list and processing methods.
¶ 5.4.10 After Printing is Completed
After printing is completed, the print head resets and stops, the printing platform automatically descends to the bottom and the screen will show 100% print progress, indicating that the printing has been completed. The model needs to be removed from the printer together with the Build Plate.

1. Unlock the door and open the front door of the chamber. If you want to end the heat preservation, enter the "Stabilization time" interface and disable the Heat Preservation option. At this time, the front door and top cover are unlocked; if you want to continue heat preservation, click the door lock button on the status bar of the screen to unlock the front door and top cover;
2. Wear gloves and take out the flexible printing Build Plate;
3. Bend the flexible printing buildplate up and down with both hands, and the print part will be separated from the buildplate.
4. Remove excess supporting material from the print part.
¶ 5.4.11 Locking of Front Door and Top Door
The printer is equipped with front door electromagnetic lock and top door electromagnetic lock. During the heating and printing process of the device, the front door and top door shall be closed. The door will be automatically locked after it is closed. Users can click the door lock icon on the main interface to unlock or lock the door.

For the safety of users, the printer always locks the front door and top lateral plate when the printing starts or the chamber starts to heat, and they cannot be opened after being locked. If you need to force unlock during this process, click the door lock button to unlock the front door and top lateral plate.
Note: Do not put your hands into the chamber after forced unlocking to avoid being scalded or pinched.
¶ 5.5 Printer Status
¶ 5.5.1 Temperature Status
| You can view the temperature status of the printer on the main interface in real time, including target temperature and real-time temperature of left extruder; target temperature and real-time temperature of right extruder; target temperature and real-time temperature of chamber; target temperature and real-time temperature of hotbed. |
 |
¶ 5.6 Software/firmware Update
¶ 5.6.1 Update through LAN
You can update the software and firmware to the latest version through LAN to improve your usage and printing experience.
The software/firmware is updated in the following steps:
|
1. Download the soft/ware/firmware package to the computer. Software package: PRO310SW_B_Vx.x.x.tar Firmware package: PRO310FW_Vx.x.x.bin |
|
| 2. Connect the computer and printer to the same LAN through Wi-Fi or network cable. Refer to 4.6.2 "Remote Print". | |
| 3. When the printer is "Connected", click the card title to enter the printer details page. |
 |
| 4. Click "Update" and select "Update Software" or "Update Firmware". |
 |
| 5. Users confirm software/firmware update without the prompt window when the printer is idle. | |
| 6. Select the software for update. |
 |
| 7. Select the firmware for update. |
 |
|
8. Click the "Select" button to select the file in the computer. Software package: PRO310SW_B_Vx.x.x.tar Firmware package: PRO310FW_Vx.x.x.bin (Note: For the package downloaded from the Internet repeatedly, remove the brackets behind its name to avoid update failure. For example, modify PRO310SW_B_V1.0.4(1).tar to PRO310SW_B_V1.0.4.tar.) |
 |
| 9. Click the "Update" button, and the package file begins to be transferred. At this point, click "Cancel" or close the prompt window, and the transfer will be interrupted. |
 |
10. The upper machine automatically disables remote print and starts to install the package file for update after receiving it.
Installation of package file for software update: Just wait for the upper machine to restart. Installation of package file for firmware update: A prompt window pops up during update, and the prompt of update completion appears in about 30 s.

There are three prompts during firmware update:
(1) Firmware update succeeded.
(2) Firmware update failed. Please re-update it. (Update failed due to power failure or unstable network connection during update.)
(3) Firmware package corrupted, please re-update it. (At the beginning of the update, the update package is detected to find that the file is corrupted. Please re-download and copy it.)
If update failed due to power failure or unstable network connection during remote update, the software and firmware will remain the version before update and be re-updated after the device restarts.

¶ 5.6.2 Update through U-disk
Software update:
1. Decompress "PRO310SW_B_V*.tar" to get two folders (namely, "openssl" and "resources") and three files (namely, "desktop", "ReleaseNote.txt", and "README.txt").
2. Copy "openssl", "resources", and "desktop" to a U-disk, and then insert the U-disk into the machine.
3. In the touch screen interface of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO, enter the "Settings" interface, click the "update" button in the "Software Version" field, and perform operation as prompted step by step.


Firmware update:
1. Copy PRO310FW_Vx.x.x.bin of the firmware to a U-disk, and then insert the U-disk into the machine.
2. In the touch screen interface of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO, enter the "Settings" interface, click the "Update" button in the "Firmware Version" field, and perform operation as prompted step by step.

¶ 6 Maintenance
Proper and regular maintenance not only helps to extend the service life of your printer, but also greatly improves your printing success rate and prototyping effect every time. This chapter describes various maintenance tasks of FUNMAT PRO 310 NEO that you need to perform.
¶ 6.1 Inspection Before Each Printing
Inspection before printing ensures the safety during printing and improves the print success rate.
¶ 6.1.1 Inspect the Printing Platform
Inspect the platform and flexible printing buildplate:
1. To ensure that the magnetic platform is free of foreign matters, there are no adsorbed debris on the magnet, and the screws for installing the magnet are not loose or protruding;
2. To check whether there is any foreign matter or damage on the surface of flexible printing Build Plate;
3. To correctly adsorb the printing buildplate on the printing platform.
¶ 6.1.2 Clean the Printing Chamber
The material filaments remaining on the buildplate of the chamber may melt in the heated chamber and stick to the buildplate, and the sundries in the chamber under the platform may occupy the movement space of Z-axis. Therefore, clean all the debris and material chips inside the printing chamber carefully before printing.
¶ 6.1.3 Inspect the Nozzle
|
To prevent the residual materials on the nozzle from affecting the prototyping quality of printing works, you should inspect whether the nozzle is clean before each printing. If it is not clean, you need to heat the extruder to the temperature that can melt the residual materials, then clean the extruder using a copper wire brush with wooden handle. If the material sticks to a higher position and enters the rubber sleeve near the nozzle, you need to remove it, clean the nozzle and then install it back. |

|
¶ 6.1.4 Check the Humidity of the Material Chamber
Phenomena such as stringing and bubbles occur when printing with damp materials, which can affect the print success rate. Therefore, the humidity of the material chamber should be checked before each print task. If the humidity in the material chamber is too high, the molecular sieve drying box should be dried and then placed in the sealed filament box for use.
Judging conditions: When the material box is closed for more than one day, the temperature and humidity indicator shows that the humidity is over 20%.
Note: The filament box can play the drying role, and the wire rod shall be dried before
usage according to the Print Process Guidelines.

|

|
Drying process: Open the upper cover of the material box to take out the drying box, and place it in the 200°C blast drying oven for drying for 2 h or a longer time; wear heatresistant gloves and take it out to prevent scalding, and place it in the material box after cooling down to the normal temperature.

¶ 6.2 Maintenance after Each Printing
¶ 6.2.1 Clean the Printing Buildplate
After printing, lower the printing platform for a certain distance, then wear gloves to take out the printing Build Plate together with the print part from the printer, bend the flexible printing buildplate with both hands to separate the print part from the printing Build Plate, and then clean the printing Build Plate and put it back on the hotbed.
¶ 6.2.2 Clean the Nozzle
Inspect whether the nozzle surface is stuck with some print materials after each printing. If the nozzle is covered by residual materials for a long time, its service life will be affected. To prepare for the next printing, pay special attention to cleanliness of the nozzle surface. If the nozzle is stuck with too many residual materials, heat the nozzle to the set temperature of the material and then clean it using a copper wire brush with wooden handle.
Note: Move the printing buildplate to the lowest position before cleaning the nozzle, and be careful to avoid scald burn risk when removing the protective sleeve to clean the nozzle.
¶ 6.2.3 Clean the Chamber
The nozzle brush scrapes some material chips into the chamber during printing. Clean the chamber carefully every time after printing a work.
¶ 6.3 Regular Maintenance
¶ 6.3.1 Replace the Nozzle
After long term of printing, the inner and outer surfaces of the nozzle can be partially worn, which affects the printing quality, especially for the printing of fiber-containing materials. Therefore, it is recommended to pay close attention to whether the surfaces of print parts get rough or whether there is visible wear deformation at the tip of the nozzle after 10 kg of materials are printed with a single nozzle. If the above phenomenon occurs, it is recommended to replace with a new nozzle.
¶ 6.3.2 Clean Feeding Gears of the Extruder
| After long-term use, more and more cut material chips accumulate in the tooth spaces of feeding gears, thus reducing the feeding force of the extruder. It is recommended to remove the front housing of the extruder every month, remove the front cover plate, and take out the feeding gear shaft 2 to inspect the accumulation of material chips in the tooth spaces of two feeding gear shafts. If necessary, you need to carefully clean each tooth space with tools such as small copper wire brush or tweezers. |

|
¶ 6.3.3 Clean the Fans
It is recommended to clean and maintain the fan at the printer mainboard and two exhaust fans on the upper rear side of the printer once every 12 months to prevent excessive dust from affecting device performance.
1. Clean the two exhaust fans on the upper rear side of the printer. Remove the rear cover of the printer, find the two exhaust fans at the upper part, and clean their blades with cleaning tools such as brushes, non-woven fabrics, and alcohol.
2. Clean the cooling fan at the printer mainboard. Remove the rear cover of the printer. The cooling fan is located directly below the main board. Remove four fixing screws to slightly remove the fan (without the need to unplug the power supply), and clean its blades with cleaning tools such as brushes, non-woven fabrics, and alcohol.
¶ 6.3.4 Maintenance of Moving Parts
It is recommended to re-apply PFPE grease or lithium soap based grease every 6 months for the X-axis and Y-axis motion guide components (The left and right lateral plates of the printer shall be removed when applying grease to the Y-axis guide rail).
1. Ensure that all relevant temperatures are set to "0" and the motor is disabled in System Settings ("Motor enable" is Off);
2. Manually move the extruder assembly to the center;
3. Clean the residual grease on the X/Y guide rail with a cloth;
4. Apply PFPE grease to the X/Y guide rail with a soft brush. Note: Excessive grease may have a negative impact on motion.
5. Move the extruder assembly back and forth several times on the X/Y axis for evenly applying the grease.

The Z-axis motion components include linear bearing and ball screw. It is recommended to re-apply PFPE grease or lithium soap based grease to the Z-axis motion components once every 6 months (The rear plates of the printer shall be removed).
1. Power off the printer and unplug the main power cord.
2. Remove the 4 locking screws at four corners of the rear cover with a wrench.
3. Apply PFPE grease or lithium soap based grease to the linear guide rail and ball screw with a soft brush. Excessive grease may have a negative impact on motion.
4. Install the rear cover back to its original position and fix it, plug in the main power cord, then turn on the printer, and move the Z-axis up and down 10 times to evenly smear the grease.
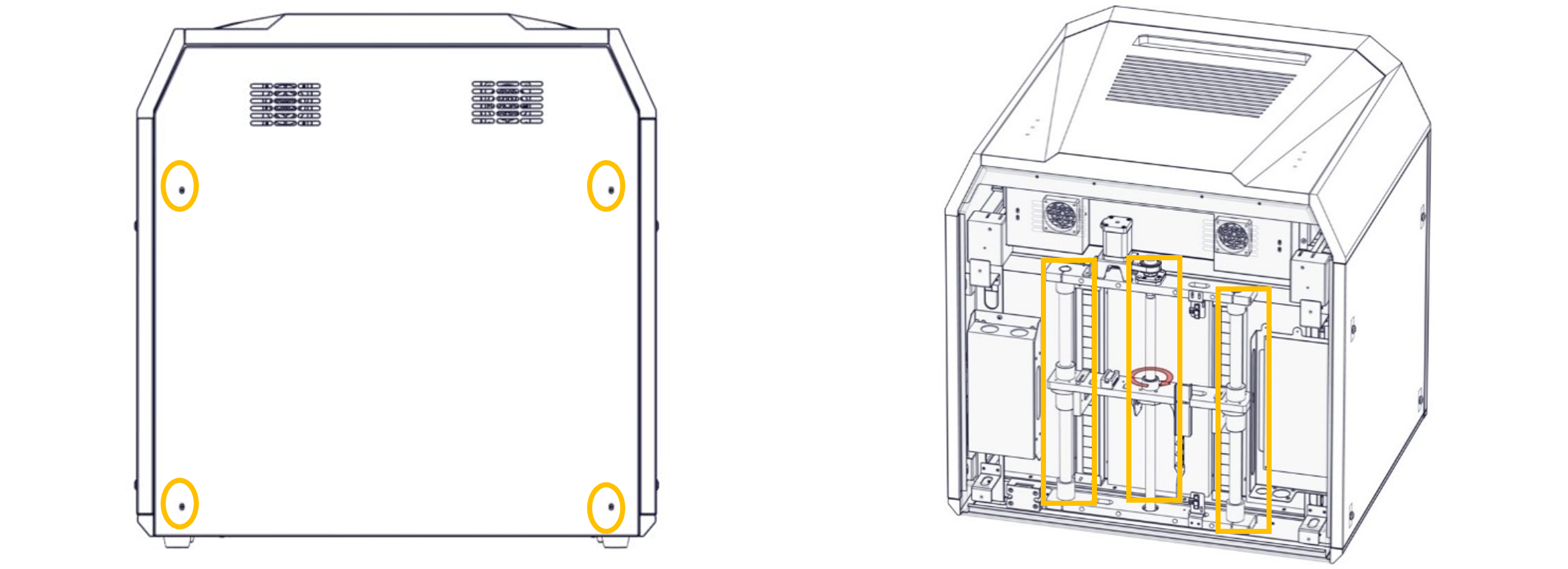
Note: Before re-applying grease on each component, wipe the surface of the kinematic pair clean with a dust-free cloth dipped in alcohol, then evenly apply grease on the surface.
¶ 6.3.5 Maintenance of Chamber Filter
Air filters are installed at the air inlets on both sides of the printing chamber. You can access the filters by unscrewing the screws of the filter cover plate and removing the cover plate. It is recommended to check or replace them every 6 months.

¶ 6.3.6 Maintenance and Replacement of Feeding Tube
The feeding pipe of the printer consists of two parts, one inside the printer and the other outside the printer. The external feeding pipe is connected to the printer from an independent filament box, and the internal feeding pipe is connected to the extruder by a material shortage detection mechanism.
As the internal feeding pipe works in a high-temperature environment, it is recommended to replace it every 12 months to avoid possible aging that may reduce its flexibility.
1. Unload the filaments and ensure that all are returned to the material compartment.
2. Turn off the printer and open the top cover, and start maintenance after the temperature of all components drops to room temperature.
3. Move the extruder assembly to the center, press down the black collar with one hand and take out the feeding pipe with the other.
4. Take out the other end of the feeding pipe from the quick connector according to Step 3.

5. Remove the external feeding pipe according to the same steps.
6. Prepare new pipes of the same length, install them in place.
Note: Both ends of the feeding pipe must be fully in place to ensure smooth threading.

¶ 6.4 Others
It is recommended to have a qualified professional conduct a thorough inspection of your printer before the one-year warranty period expires. The inspection should include checking whether the fans, heater, power supply, fuse, and other components are in normal condition. If any issues are found, contact our local agent, refer to the INTAMSYS Help Center:https://help.intamsys.com/
or scan the QR code:

Some protective components might need to be removed during inspection to make the components to be inspected observable. Be careful because these operations pose a certain safety risk.
In addition, you can download the latest version of firmware and screen software from the following website:
https://www.intamsys.cn/
¶ 7 Trouble shooting
This chapter lists some faults that might occur during printing and required troubleshooting measures after each fault occurs.
If you have any question during operation based on this user manual, contact the Customer Support in the region where you are located.
Table 8.1 Fault Code List
| S/N | Code | Error Message | Type | Measures |
| 1 | 171 | Serial port communication error | error | If possible, please continue printing. If there is no response for a long time, please shut down and restart the printer |
| 2 | 217 | Material shortage of left extruder | warning | Please replace the material or insert the material into the out-of- filament detection sensor |
| 3 | 218 | Material shortage of right extruder | warning | Please replace the material or insert the material into the out-of-filament detection sensor |
| 4 | 221 | Opening of chamber front door | warning | Close the front door. |
| 5 | 222 | Opening of chamber top door | warning | Close the top door. |
| 6 | 235 | Extruder leveling sensor abnormal | warning | Extruder calibration and automatic leveling cannot be carried out. Please check whether the extruder leveling sensor is disconnected or whether the connector is loose |
| 7 | 301 | Overhigh temperature of L-Nozzle | error | Check the L-Nozzle sensor or heater. |
| 8 | 302 | Overhigh temperature of R-Nozzle | error | Check the R-Nozzle sensor or heater. |
| 9 | 303 | Overhigh temperature of hotbed | error | Check for exception in the cable or connector of hotbed sensor |
| 10 | 304 | Overhigh temperature of chamber | error | Check for exception in the cable or connector of chamber sensor |
| 11 | 306 | Damaged circuit of L Nozzle temperature sensor | error | Check the circuit of L-Nozzle temperature sensor. |
| 12 | 307 | Damaged circuit of R Nozzle temperature sensor | error | Check the circuit of R-Nozzle temperature sensor. |
| 13 | 308 | Damaged circuit of hotbed temperature sensor | error | Check the circuit of the hotbed temperature sensor. |
| 14 | 312 | Too slow temperature rise of L-Nozzle | warning | Check whether the heater is damaged or the wiring has exceptions |
| 15 | 313 | Too slow temperature rise of R-Nozzle | warning | Check whether the heater is damaged or the wiring has exceptions |
| 16 | 314 | Hotbed heating timeout | error | For heating timeout, check for exceptions in the heating circuit |
| 17 | 315 | Chamber heating timeout | error | For heating timeout, check for exceptions in the heating circuit |
| 18 | 332 | X-limit sensor triggered | error | Please confirm whether the printing is staggered or the model exceeds the printing size of the printer |
| 19 | 333 | Y-limit sensor triggered | error | Please confirm whether the printing is staggered or the model exceeds the printing size of the printer |
| 20 | 334 | Z-limit sensor triggered | error | Please confirm whether the leveling is normal or whether the model exceeds the printing size of the printer |
| 21 | 391 | The instruction cannot be completed without resetting | error | Resetting operation is required in axis control |
| 22 | 366 | Motor driver alarm | error | Check the XYZ motor driver. |
| 23 | 368 | Motor drive alarm | error | Check the E motor drive for any problems. |
| 24 | 369 | SPI error of motor drive | error | Check the E motor drive for any problems. |
| 25 | 397 | Extruder temperature update error | error | Check whether the extruder temperature is updated. |
| 26 | 398 | Incorrect G-code motion data | error | Check whether G-code motion exceeds the maximum single motion criterion. |
| 27 | 406 | Power-off protection triggered by the system for the power supply voltage is lower than 90% of the supply voltage | error | Continue printing after power failure. The firmware detects power failure during printing, and 406 alarm will be given after the device is powered on again. |
FOLLOW INTAMSYS ON


www.intamsys.cn
info@intamsys.com
| HEADQUARTERS: | BRANCH: | BRANCH: |
| INTAMSYS Technology Co., LTD | INTAMSYS TECHNOLOGY GmbH | INTAMSYS Technology, US. |
| Address: Address:1&4F, Building 2, No.24&26 Gubo Road Pudong New District, 201316 Shanghai China | Address: 35, Zeppelinstr., 73760 Ostfildern Deutschland | Address: 1884 Berkshire Lane N, Plymouth MN 55441,United States |
| Copyright ©2023 INTAMSYS Technology. All rights reserved. The information at hand is provided as available at the time of printing, INTAMSYS reserves the right to change any information without updating this publication. | ||